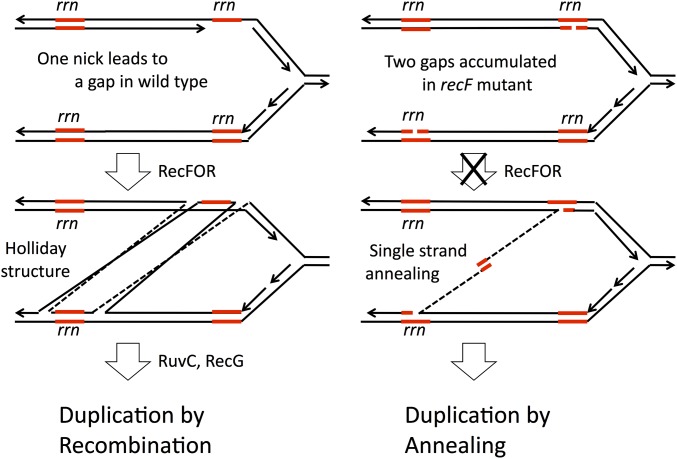
Figure 9.
Formation of duplications at gaps by RecFORA recombination and by annealing in recF mutants. The model assumes that duplications are normally made primarily by the RecFORA pathway and are initiated by nicks within the rrn sequence. Strand exchange leads to Holliday structures that can be resolved to produce a duplication (left). In the absence of RecFORA, unrepaired nicks and gaps accumulate in both rrn cistrons and can produce single strands that are uncoated by RecA and available for formation of duplications by single-strand annealing (right). Activation of this pathway by recF mutation renders the RuvC and RecG enzymes dispensable and allows suppression of a ruvC, recG double mutation.