FIGURE 6.
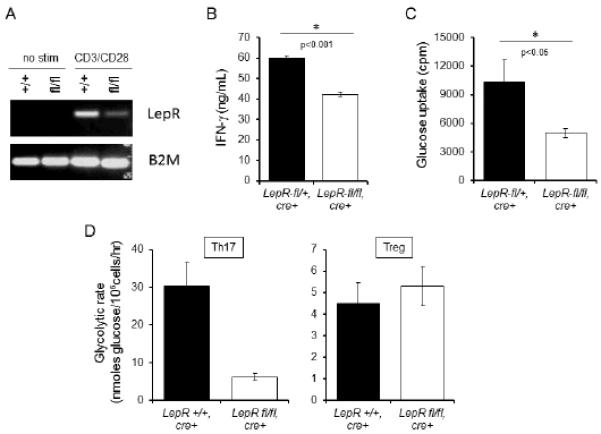
T cell-intrinsic leptin receptor signaling is required for activated T cell inflammatory cytokine production and glucose metabolism. (A) T cell-specific leptin receptor (LepR) conditional knockout was generated using cre-lox recombination. LepR expression was determined by RT-PCR using primers to LepR and beta-2-microglobulin (control). (B and C) CD4+ T cells were isolated from conditional LepR knockout (white bar) versus heterozygous control mice (black bar) and activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for 48 hours, after which glucose uptake was assessed (B) and IFN-γ concentration was measured in culture supernatants by ELISA (C). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) CD4+ T cells were isolated from CD4+ T cell specific conditional LepR knockout (white bar) and homozygous control mice (black bar) and induced to differentiate into Th17 and Treg populations in vitro, after which glycolytic rate was determined. Data are representative of two independent single mouse experiments.
