FIGURE 8.
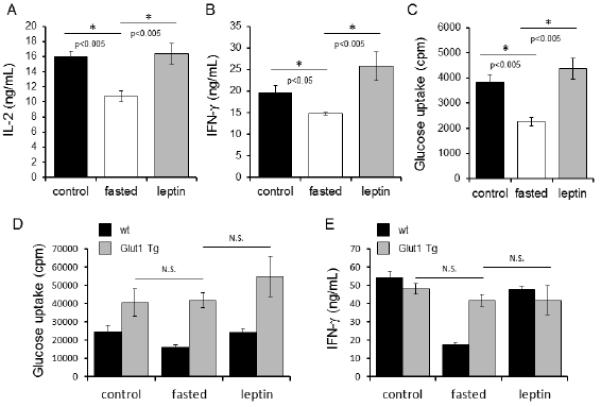
Both in vivo leptin administration and Glut1 overexpression can rescue peripheral T cell function and metabolism in fasted mice. (A-C) CD4+ T cells were isolated from control C57BL/6J mice (black bars), fasted mice (white bars), or fasted mice receiving leptin injections (grey bars), and activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for 48 hours, after which cytokine production was measured by ELISA (A and B) and glucose metabolism was analyzed by comparing relative glucose uptake (C). Data are representative of two independent experiments; three mice per experimental group. (D and E) Wildtype C57BL/6J mice (black bars) or T cell-specific Glut1 transgenic mice (Glut1 Tg; grey bars), were either fed ad libitum (control), fasted, or fasted while receiving leptin injections (leptin), as indicated, for 48 hours. Peripheral CD4+ T cells were isolated and activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for an additional 48 hours, after which glucose metabolism was analyzed by measuring glucose uptake (D) and IFN-γ production was measured in culture supernatants by ELISA (E). Data are representative of two independent experiments, three mice per group.
