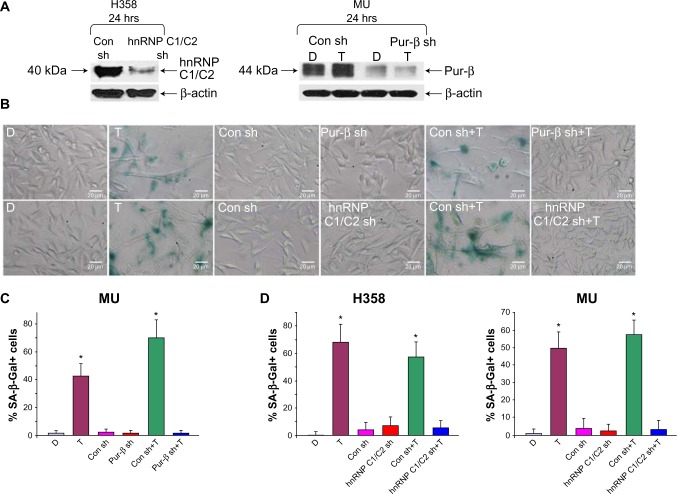
Figure 3.
Knockdown of hnRNP C1/C2 and Pur-beta decreased T-oligo-induced senescence in H358 and MU cells.
Note: (A) Transfection of shRNA against hnRNP C1/C2 for 24 hours led to a 3.5-fold decrease in hnRNP C1/C2 expression in H358 cells. shRNA-mediated knockdown of Pur-beta decreased Pur-beta expression by 3.0-fold and prevented T-oligo-induced upregulation of Pur-beta after 24 hours in MU cells. (B) After exposure to T-oligo for 1 week, MU cells deficient in hnRNP C1/C2 and Pur-beta were stained for the presence of senescence-associated beta-galactosidase and images were taken with a 10× objective lens. (C and D) Knockdown of Pur-beta in MU melanoma cells reduced the ability of T-oligo to induce senescence by 19.3-fold, when compared with cells exposed to T-oligo after transfection with control shRNA. Further, hnRNP C1/C2-deficient H358 and MU cells treated with T-oligo displayed a 14.8- and 12.5-fold decrease in senescence, respectively, in comparison to cells exposed to T-oligo after transfection with control shRNA. *P<0.001.
Abbreviations: hnRNP C1/C2, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C1 and C2; Pur, purine-rich element binding protein; shRNA, short hairpin ribonucleic acid; Con sh, control shRNA; C1/C2 sh, hnRNP C1/C2 shRNA; D, diluent; T, T-oligo; SA-β-Gal, senescence-associated beta galactosidase.