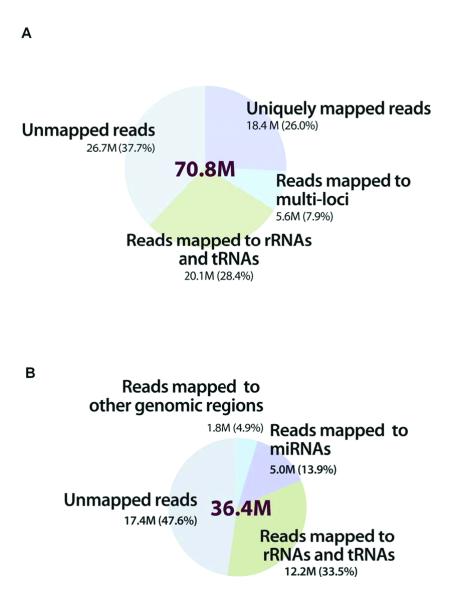
Figure 1. Distribution of short reads in the WT-seq and small RNA-seq datasets when mapped to the human reference genome.
(A) WT-seq dataset of 2.1 billion 50-nt short reads from the 30 samples. Using the ABI Bioscope™ (version 1.21) WT-seq analysis pipeline, 62.3% of the short reads were mappable: 28.4% were mapped to the sequences of no biological interest (e.g., rRNAs and tRNAs) and were therefore filtered; and 26.0% (18.4 million per sample) were uniquely mapped to the human reference genome (hg19) or exon junctions. (B) Small RNA-seq dataset of 894 million 35-nt short reads, mean of 36.4 million reads from the 25 samples. Using the SOLiD System Small RNA Analysis Pipeline Tool, 52.4% of the short reads were mappable; 33.6% mapped to sequences of no biological interest were removed from further analysis. On average 13.9% (5.1 million per sample) were mapped to known miRNAs in the miRBase database (version 13.0).