Fig. 6.
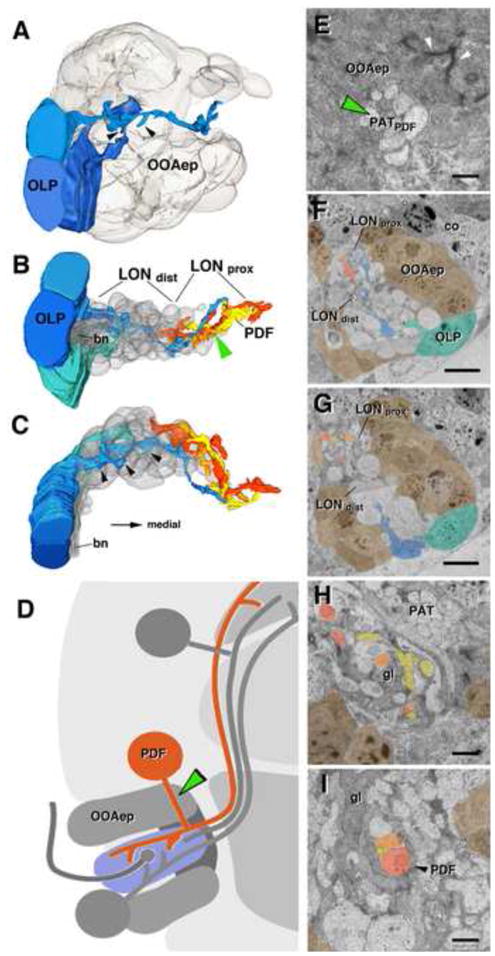
Projection neurons of the larval optic neuropil (LON). A–C: 3D digital models of LON, showing optic lobe pioneers (OLP) in shades of blue, and PDF-dendritic branches (PDF) in shades of orange, yellow and red; cellbodies of the outer optic anlage epithelium (OOAep) are translucent grey. The same colors are used in panels E–I, which show TEM sections of LON at different levels. Cell bodies of OLPs are located laterally adjacent to OOAep, flanking the entering Bolwig’s nerve (bn) (A, F, G). Note multiple short, dendritic branches of OLP fibers, preferentially in distal LON (LONdist; arrowheads in A–C). PDF neuritis are found preferentiall in the proximal LON (LONprox) and LONdist. Cell bodies of PDF neurons, shown schematically in (D), are located dorsally adjacent to the OOA. Cell body fibers form a bundle (PATpdf) that penetrates through the OOA epithelium (green arrowhead in D and E; represents a section of the OOA epithelium near its outer, apical boundary; note sub-apical adherens junctions shown by white arrowheads). Cortex neuron cell body (co) flanking the OOAep (in E). PDF-neuronal fibers form bundle in proximal LON (arrowhead in I) and extend branches throughout this compartment (B, C, F, G, H), glia cells (gl), PAT primary lineage related axon tract (I, H). Scale bars: 2 μm (F, G), 1μm (H, I, E).
