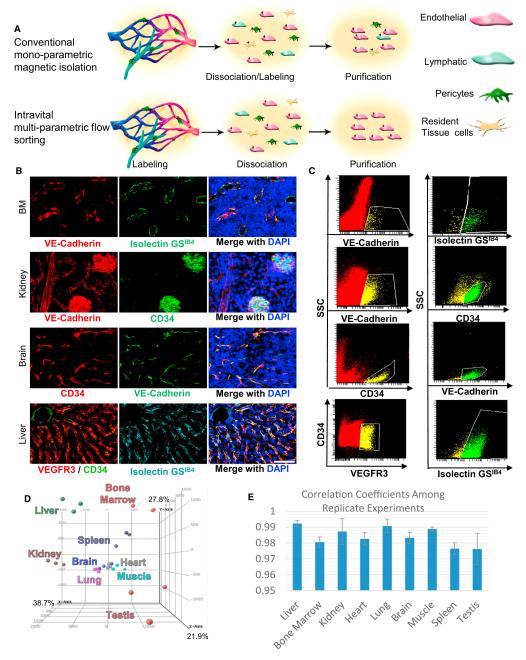
Figure 1. Determination of Tissue-Specific Vascular Signature of ECs Purified by Intravital Staining.
(A) Schematic model of conventional EC isolations utilizing magnetic beads after tissue dissociation compared to intravital labeling with multiple fluorescent markers in vivo, which results in enhanced purities.
(B) Wild-type (WT) animals were coinjected with fluorescently labeled antibodies and IsolectinGSIB4 8 min prior to sacrifice. Primary channels (left) provided for the clearest resolution of the ECs, secondary channels (middle) confirmed the cell as EC via microscopy. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (right).
(C) The identical markers from (B) were applied to flow cytometric analysis. Tissues from intravitally labeled animals were enzymatically dissociated. Red cells noted in the scatterplots only include live single cells without highly autofluorescent, nonspecific IgG binding cells, or aggregates of two or more cells. Cells highlighted in yellow are positive for the primary-specific EC marker and then interrogated in a secondary channel. Double positive cells are shown in green.
(D) Genome-wide principal component analysis (PCA) of the nine tissues profiled showing the individual replicates from each tissue. Tissues are color-coded corresponding to their label.
(E) Correlation coefficients are presented for the transcriptional profiling among the biological triplicates demonstrating high fidelity. Scale bars represent 100 μm, error bars represent SD.
See also Figures S1 and S2.