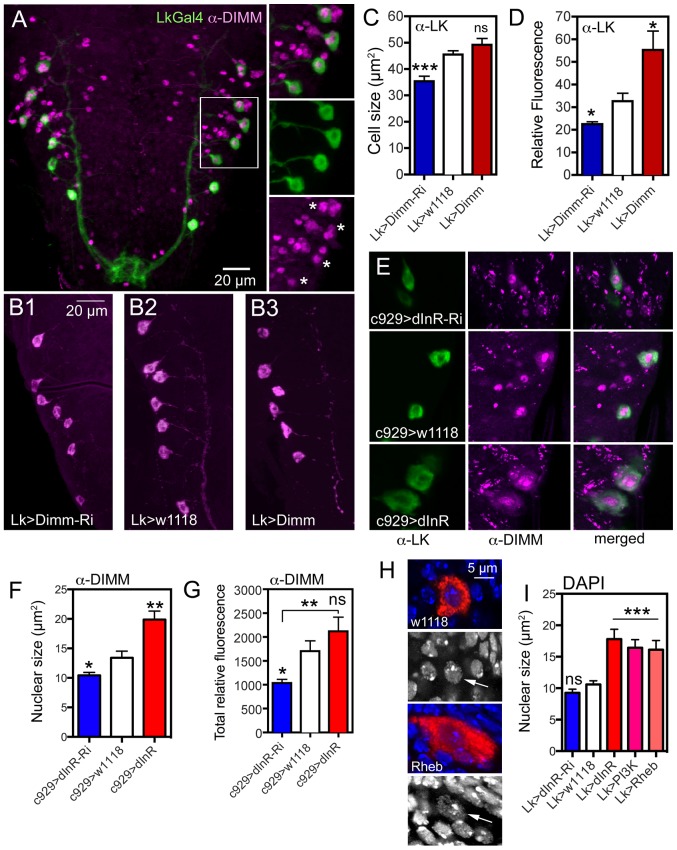
Figure 9. Possible interactions between Dimm and dInR in ABLKs and effects on nuclear size.
A. The ABLKs (Lk-Gal4-GFP; green) express DIMM-immunolabeling (magenta) in nuclei. Details of the framed area are shown in smaller panels (asterisks indicate nuclei of LK neurons). B–C The size of LK cell bodies diminishes with Lk-Ga4 driven Dimm-RNAi, but is not affected by Dimm overexpression (***p<0.001, n = 6–9 animals from 3 crosses for each genotype; unpaired Student's T-test). D The LK-immunofluorescence in ABLKs is affected by both Dimm-RNAi and over expression (*p<0.05, n = 6–9 flies for each genotype from 3 crosses; unpaired Student's T-test). E and F Manipulations of dInR using the c929-Gal4 affects nuclear size as determined by DIMM immunolabeling (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, n = 7–8 animals for each genotype from 3 crosses: unpaired Student's T-test). The surface area of each DIMM-labeled nucleus in LK-immunolabeled cell bodies (in A1–A4 segments) was measured using Image J and the average nuclear size (LK-neurons in A1–A4) of each fly was thereafter determined. G The total fluorescence (mean fluorescence multiplied by cell size) in abdominal DIMM immunolabeled neurons decreases with dInR-RNAi, but there is no significant increase after dInR over expression (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, n = 8 animals for each genotype from 3 crosses; unpaired Student's T-test). H and I Effects of dInR, PI3K and Rheb manipulations on size of nuclei in ABLKs. In H nuclear size is visualized by DAPI staining (blue) in ABLK neurons (red). Nuclear size (arrows) is enlarged after Rheb over expression. I Quantification of nuclear size shows that dInR-RNAi has no effect (compared to controls), whereas over expression of dInR, PI3K and Rheb produces a significant enlargement of nuclei (unpaired Student's T-test, *** p<0.001, n = 6–11 animals for each genotype from 3 crosses).