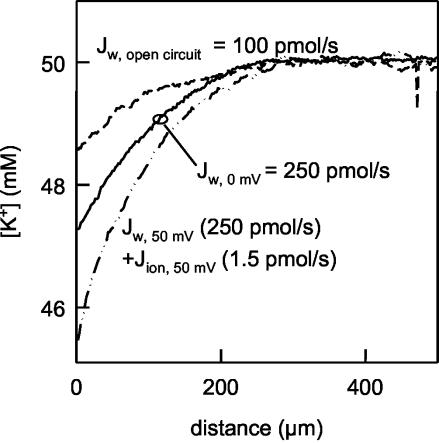
Fig. 1.
Water and ion fluxes through planar bilayers reconstituted with purified KcsA. The K+ flux was equal to 1.5 pmol/s at a stationary potential of 50 mV, as revealed by current measurements. It was accompanied by a voltage-insensitive water flux of at least 250 pmol/s, as derived from the K+ dilution in the immediate vicinity of a membrane clamped to 0 mV. Cation polarization was measured by scanning microelectrodes at the indicated distances from planar lipid bilayers. In an open circuit, there is no ion transport across a membrane containing only cation-selective channels. Because of the single-file nature of transport, water flow is inhibited also. It is conducted only by the lipid bilayer, which enables a flux of 100 pmol/s. The buffer contained 50 mM KCl, 100 mM choline chloride, 100 μM MgCl2, and 10 mM Hepes. Osmotic water flux was induced by 1 M urea.