Figure 1.
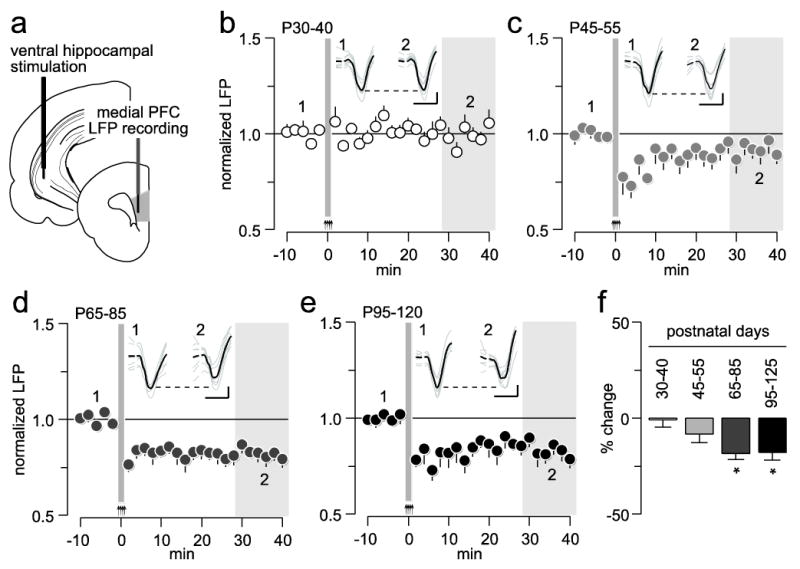
Age-dependent effects of ventral hippocampal high-frequency stimulation (HFS)-induced plasticity in the medial prefrontal cortex (PFC). (a) Diagram depicting the recording arrangement used to study hippocampal-induced plasticity in the medial PFC by means of local field potential (LFP) recordings. (b) Effects of ventral hippocampal high-frequency stimulation (HFS) on medial PFC LFP in postnatal days (P) 30-40 rats (n=7). Arrows and area marked in gray at 0 minute (min) indicate the HFS period. (c) Effects of ventral hippocampal HFS on medial PFC LFP in P45-55 rats (n=7). (d) Effects of ventral hippocampal HFS on medial PFC LFP in P65-85 rats (n=7). (e) Effects of ventral hippocampal HFS on medial PFC LFP in P95-120 rats (n=7). (f) Bar graph summarizing the mean LFP response from the 30-40 min post-HFS (area marked in gray shown in b, c, d, and e; *p<0.02 vs. P30-40, Tukey post-hoc test). Insets: example traces of ventral hippocampal-evoked LFP before (1) and after (2) HFS (calibration bars: 3 mV, 50 ms).
