Figure 3.
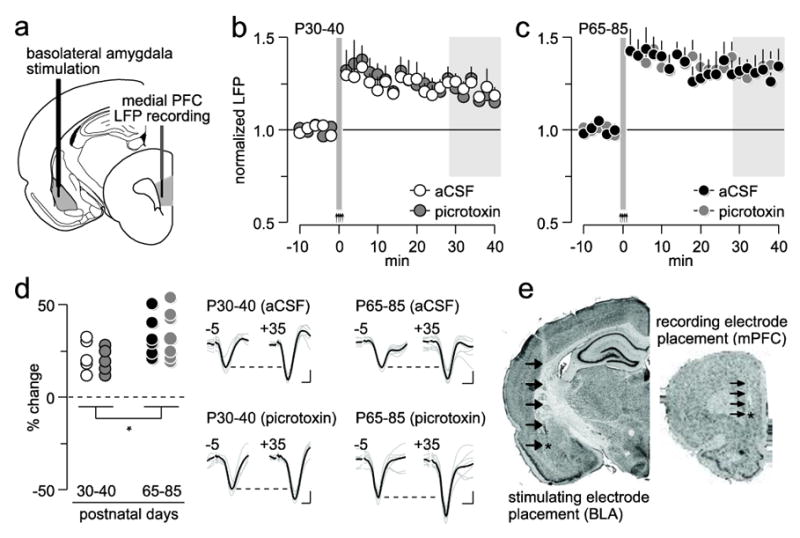
Role of local prefrontal GABAergic function in the regulation of basolateral amygdala-induced plasticity in the medial PFC. (a) Diagram depicting the recording arrangement used to study the effects of basolateral amygdala HFS on medial PFC LFP. (b) Effects of local PFC microinjection of aCSF (n=5) or picrotoxin (n=5) on basolateral amygdala HFS-induced prefrontal LTP in P30-40 rats. (c) Effects of local PFC microinjection of aCSF (n=7) or picrotoxin (n=7) on basolateral amygdala HFS-induced prefrontal LTP in P65-85 rats. (d) Summary of the mean LFP response obtained from the 30-40 min post-basolateral amygdala HFS period (area marked in gray shown in b and c; *p=0.02, main age effect). Insets traces are examples of basolateral amygdala-evoked LFP taken from 5 min pre-HFS (-5) and 35 min post-HFS (+35) illustrating the impact of picrotoxin on PFC plasticity (calibration bars: 3 mV, 50 ms). (e) Examples of cresyl violet-stained coronal sections obtained from a picrotoxin-infused P65-85 rat showing the location of the recording (mPFC: medial PFC) and stimulating (BLA: basolateral amygdala) electrodes. Arrows indicate the track of the electrode placement.
