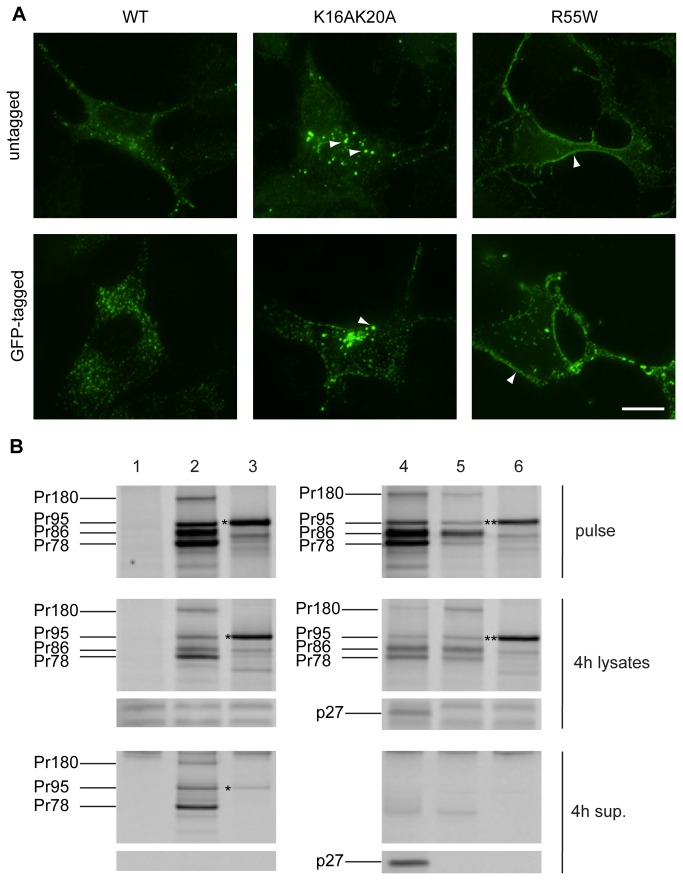
Figure 4. Comparison of untagged and GFP-tagged M-PMV Gag wild-type and mutants in COS-1 cells.
(A) COS-1 cells were cotransfected at the ratio of 4:1 with pSARM-WT and pSARM-GagGFP-M100A, pSARM-R55W and pSARM-GagGFP-M100A-R55W, or pSARM-K16A/K20A and pSARM-GagGFP-M100A-K16A/K20A (tagged) or transfected with the untagged pSARM-WT, pSARM-R55W or pSARM-K16A/K20A mutants (untagged). Cells were fixed 24 h post-transfection with cold methanol:acetone (1:1). Cells transfected with untagged provirus were stained by primary rabbit antibody against M-PMV p27 and secondary FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody. Localization of K16A/K20A mutant into intracellular vesicles and localization of R55W on plasma membrane is shown. Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) COS-1 cells (untransfected, Lane 1) were transfected with pSARM-D26N (Lane 2), pSARM-GagGFP-M100A (Lane 3), pSARM-X (Lane 4), pSARM-R22A (Lane 5) and pSARM-GagGFP-M100A-R22A (Lane 6). Viral proteins were metabolically labeled with [35S] and then immunoprecipitated with goat anti-MPMV antibody from lysates of pulse-labeled cells (pulse), pulse-labeled and 4h chased cells (4h lysates) and from the culture medium collected after the 4h chase (4h sup.). Positions of the viral precursor proteins Pr180 (Gag-Pro-Pol), Pr95 (Gag-Pro), Pr86 (Envelope) and Pr78 (Gag) are shown. Products of pSARM-GagGFP-M100A (*) and pSARM-GagGFP-M100A-R22A (**) are shown.