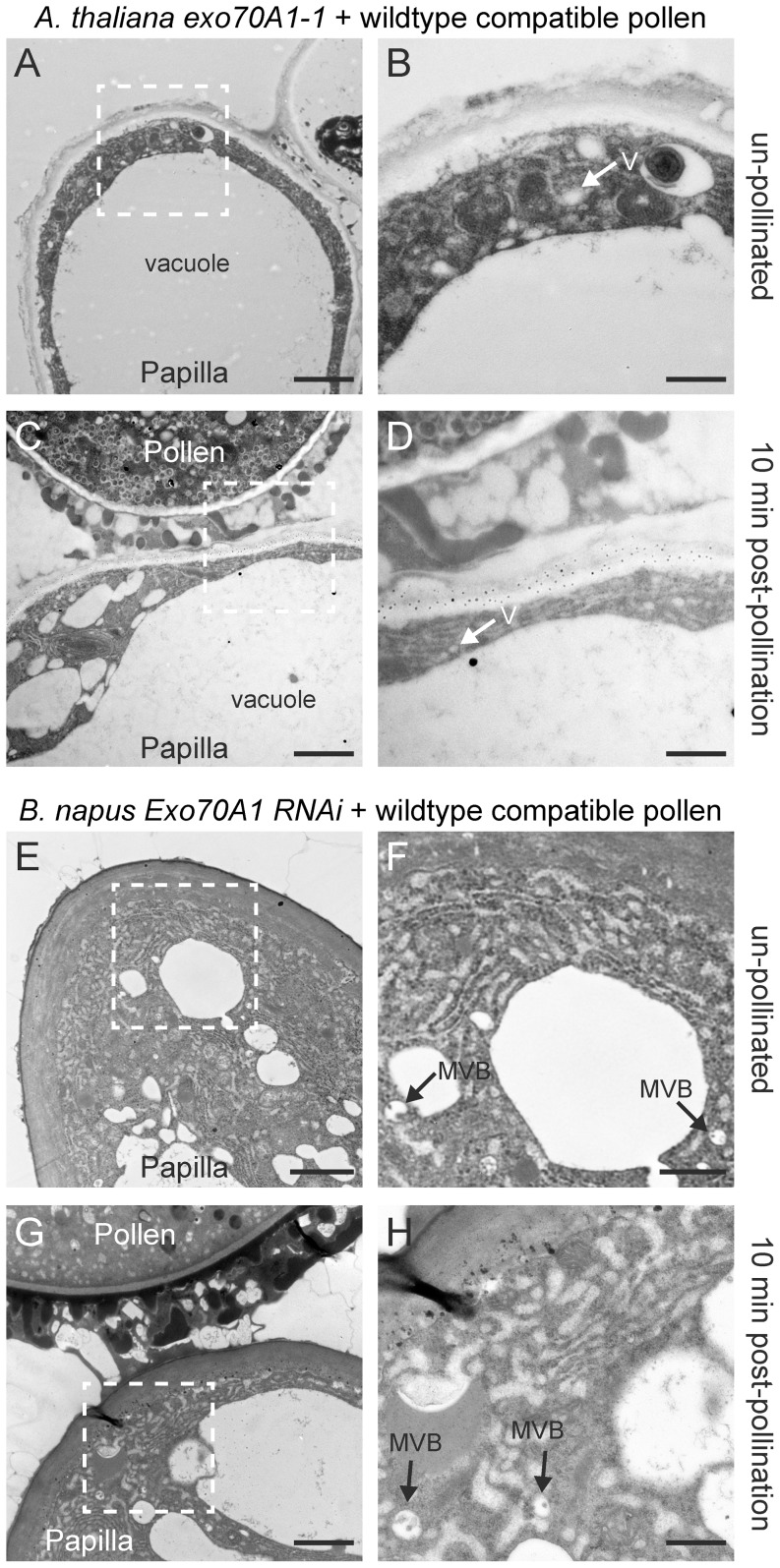
Figure 6. TEM images of A. thaliana exo70A1-1 and B. napus Westar Exo70A1 RNAi stigmatic papillae in response to wild-type compatible pollen.
(A, B) Unpollinated stigmatic papilla from the A. thaliana exo70A1-1 mutant. Some vesicle (V) accumulation was observed in the cytoplasm in 10/10 samples. (C, D) Stigmatic papilla from the A. thaliana exo70A1-1 mutant at 10 min following pollination with compatible A. thaliana Col-0 pollen. An accumulation of secretory vesicles (V) in the papillar cytoplasm was observed under the pollen contact site in 10/10 samples. (E, F) Unpollinated stigmatic papilla from the B. napus Westar Exo70A1 RNAi R2 line. Some accumulation of MVBs was observed in the cytoplasm in 10/10 samples. (G, H) Stigmatic papilla from the B. napus Westar Exo70A1 RNAi R2 line at 10 min following pollination with compatible B. napus Westar pollen. Some MVBs were observed in the papillar cytoplasm in 8/10 samples. For 2/10 samples, MVBs were observed in the cytoplasm and fusing to the plasma membrane (Figure S2C, D) which is consistent with these plants displaying an incomplete knockout phenotype [17]. The white boxed areas in (A, C, E, G) are shown in the (B, D, F, H), respectively. Scale bars (A, C, E, G) 1.5 µm; (B, D, F, H) 500 nm.