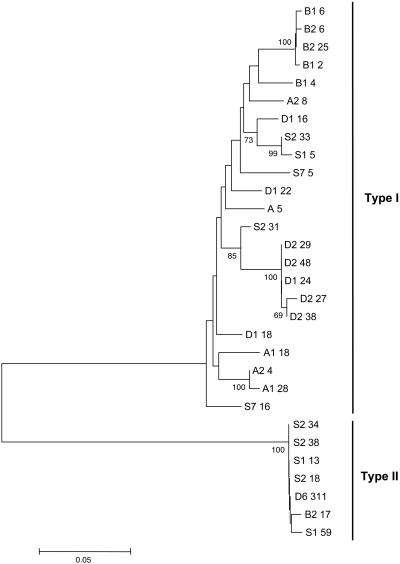
Fig. 1.
csd genealogy based on neighbor-joining analysis of genetic differences obtained from the deduced amino acid sequence, excluding ambiguous sites in which gaps have to be introduced in the alignment. The sequences fall into two major branches, types I and II. Fifteen allelic lineages were found; other sequences represent replicate variants of the same lineage, as indicated by bushes at the end of some tips (see text for further details). A genealogy of nearly identical topology was obtained when a hypervariable repeat region (rich in NY) was included. Numbers to the left of allele and replicate numbers indicate bootstrap percentages (of 1,000 resamplings) in support of each note. Bootstrap values <90% were not included. The scale bar indicates amino acid differences per site. Geographical origin is indicated by letter: D, Davis; B, Berlin; S, Stellenbosch; and A, Ribeirão Preto.