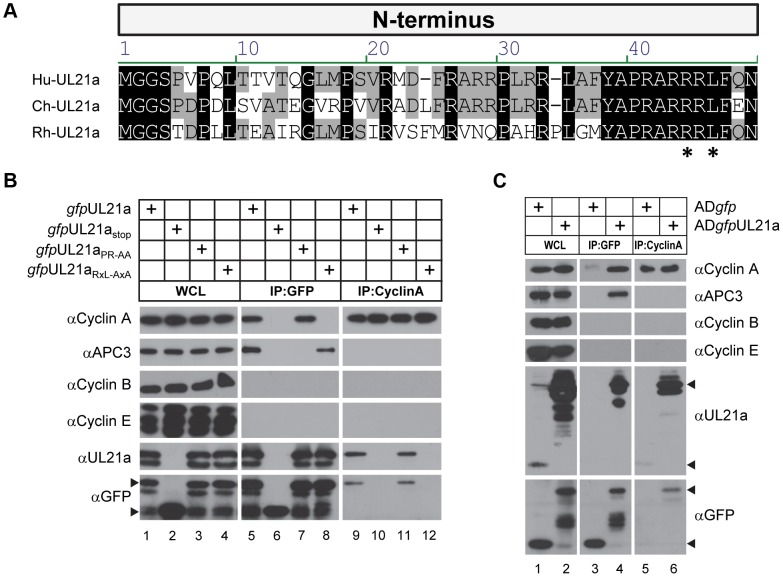
Figure 1. HCMV pUL21a interacts with cyclin A through its cyclin-binding domain.
(A) Alignment of the N-terminus of the UL21a coding sequence from HCMV (top), ChCMV (middle) and RhCMV (bottom). Asterisks denote the residues of the RxL motif that were subject to mutagenesis. (B) 293T cells were transfected with construct expressing a GFP tagged version of wildtype (gfpUL21a), stop mutant (gfpUL21astop), APC-binding domain mutant (gfpUL21aPR-AA), or cyclin-binding domain mutant (gfpUL21aRxL-AxA) pUL21a. Lysates were collected at 72 hours post infection (hpi), and immunoprecipitated with GFP or cyclin A antibody. Cell lysates and eluted proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. Arrow indicates free GFP (bottom) or GFP-tagged pUL21a (top). Partial proteolysis was often seen with the GFP-tagged UL21a protein. (C) MRC-5 cells were infected with wildtype HCMV expressing free GFP (ADgfp) or GFP-tagged UL21a (ADgfpUL21a). Lysates were collected at 48 hpi and immunoprecipitated with GFP or cyclin A antibody. Cell lysates and eluted proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. Arrow indicates free GFP, native pUL21a, or GFP-tagged pUL21a.