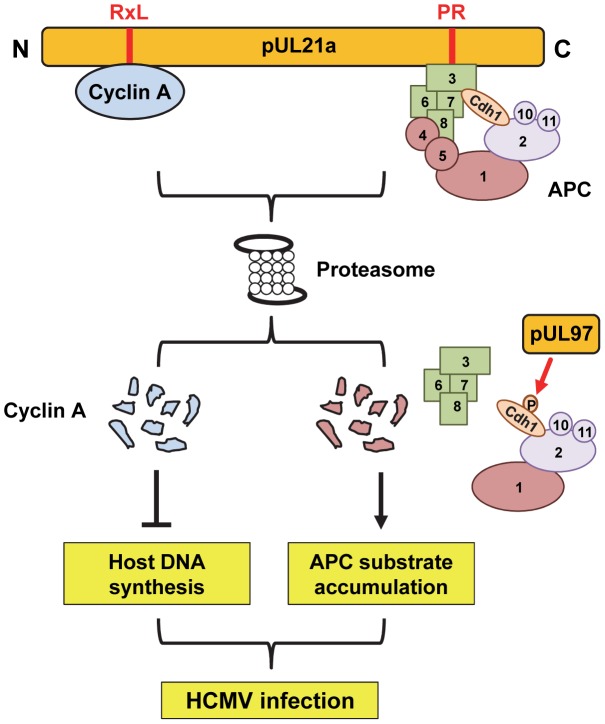
Figure 7. Model for dual roles of pUL21a in HCMV infection.
pUL21a independently binds to cyclin A or the anaphase-promoting complex (APC) through the RxL or PR domain, respectively, and targets each for proteasome-dependent degradation. pUL21a-induced degradation of the APC bridge, in concordance with pUL97-induced phosphorylation of Cdh1, leads to an increase in APC substrates, which helps to create a favorable, S-phase like cellular environment for DNA synthesis. However, pUL21a-induced degradation of cyclin A allows HCMV to specifically prevent host DNA synthesis. Together, these two independent activities of pUL21a help to subvert host cells for efficient HCMV growth.