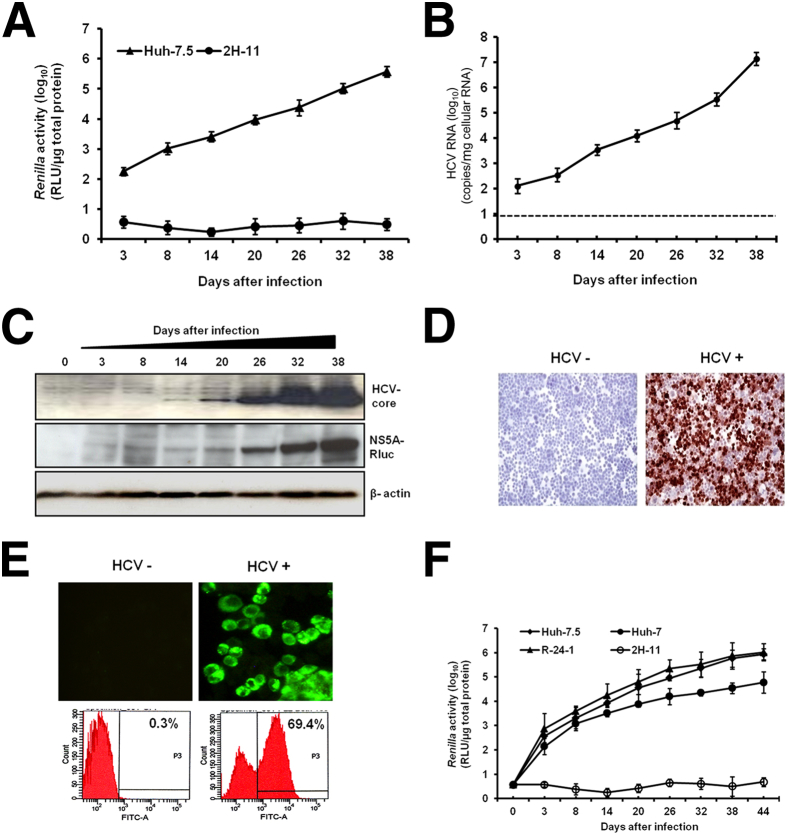
Figure 1.
Establishment of a stable and persistently infected HCV replication system in Huh-7.5 cells. Cells were infected with MOI = 0.1 JFH-ΔV3-Rluc virus overnight. The infected cells were cultured in DMEM with 10% (v/v) FBS, with passage every 6 days. A: The Renilla luciferase activity of infected cell lysates measured up to 38 days in culture indicates HCV replication after infection. The human fibroblast cell line (2H-11) was used as a negative control. B: HCV RNA level in the infected culture over 38 days. The dotted line indicates the limit of detection of the assay. C: HCV Core and NS5A–Rluc protein levels by time after infection, measured by Western blotting, with β-actin as a loading control. D: Immunocytochemical staining of uninfected (HCV−) and infected (HCV+) Huh-7.5 cells, using a monoclonal antibody specific for HCV Core protein; positive staining is reddish-brown. E: HCV Core protein was detected by immunofluorescence; the presence of HCV+ cells was confirmed by flow cytometric analysis and is reported as the percentage of HCV+ cells in the infected culture. F: Infectivity assay of culture supernatants was performed using three different hepatic cell lines (R-24-1 is an IFN-α–resistant Huh-7 cell line) and one nonhepatic cell line (2H-11). Cells were infected with 1 mL of MOI = 0.1 culture supernatant overnight, washed, and then cultured with growth medium. Cells were passaged at 6-day intervals, and Renilla luciferase activity of cell lysates was measured. Data are expressed as means ± SD. Original magnification: ×20 (D); ×40 (E). FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; RLU, relative light units.