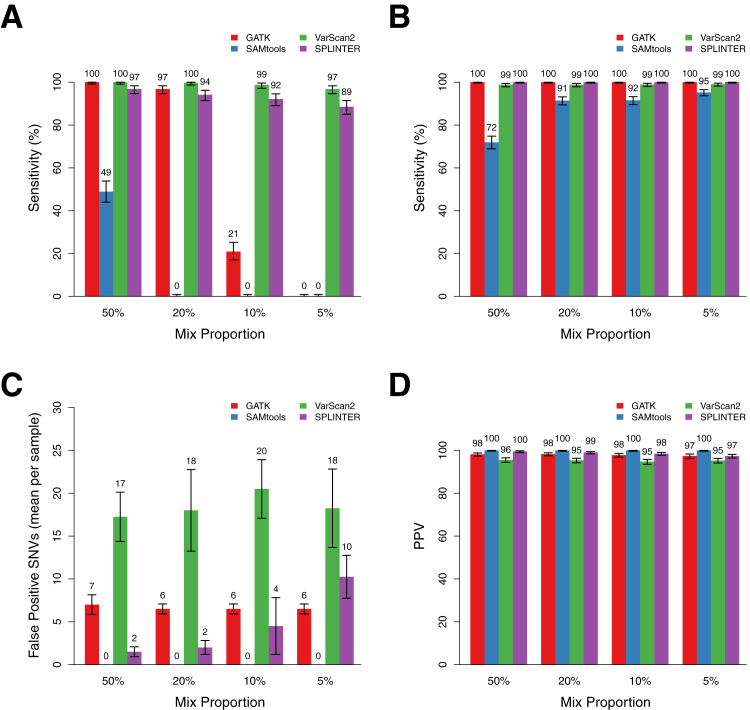
Figure 2.
Performance of GATK, SAMtools, VarScan2, and SPLINTER for detecting low-frequency variants in mixed samples at positions with coverage ≥100×. A: Sensitivity for detecting all heterozygous minor gold standard variants in samples with mix proportions of 50%, 20%, 10%, and 5% (mean observed gold standard VAFs, 25.5%, 11.2%, 6.8%, and 4.2%, respectively). Sensitivities (True positive/True positive + False negative) are point estimates based on detection of all minor gold standard variants at positions with ≥100× coverage in each set of mixed samples (n = 409, 406, 409, and 411, respectively). Error bars show the 95% binomial CI for each point estimate. B: Sensitivity for detecting homozygous and heterozygous gold standard variants in the major sample, which have estimated VAFs of >25%. Error bars show the 95% binomial CI for each point estimate. C: Mean number of false positive SNV calls per sample made by each program at the indicated mix proportion across the entire target region, encompassing coding and noncoding sequence of 26 genes (306,336 bp). Indel calls were excluded, as were positions with low coverage or discordant calls in the gold standard variant analysis (see Materials and Methods). Error bars show the SD across all samples with the indicated mix proportion (n = 4 for each mix proportion). D: PPV (True positive/True positive + False positive) for SNV calls by each program across the mix proportions. Error bars show the 95% binomial CI for each point estimate.