FIGURE 5.
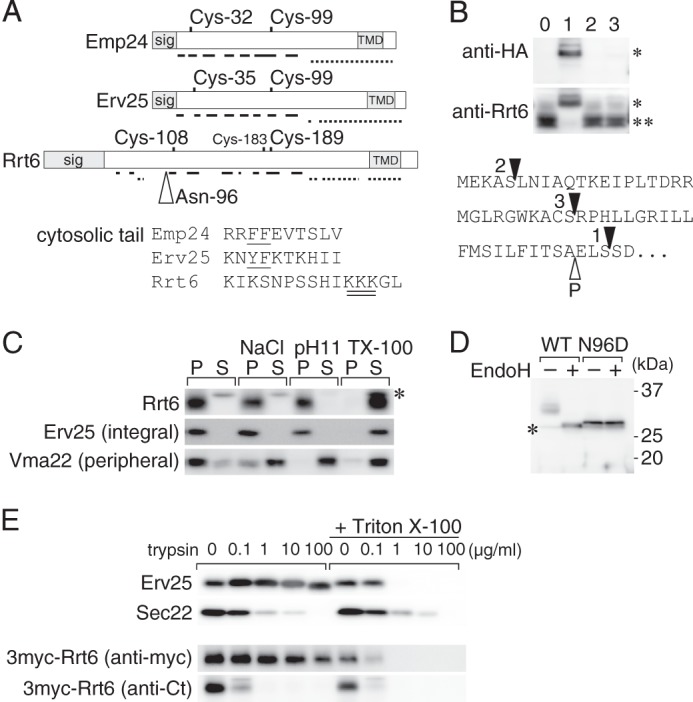
Rrt6 is structurally related to the known p24 proteins. A, schematic representations of Emp24, Erv25, and Rrt6. Location of the signal peptide (sig), the two invariably conserved cysteine residues, and the transmembrane domain (TMD) are shown. Solid and broken lines represent regions predicted to form β-strands and α-helices, respectively (57). Rrt6 has three cysteine residues (Cys-108, -183, and -189) in the luminal domain. Of these, Cys-108 and -189 appeared to correspond to the conserved cysteine pair (see text). The open triangle indicates the N-glycosylation site (Asp-96) of Rrt6. An alignment of the cytosolic tail sequences of the three proteins is also shown. In the alignment, amino acids were expressed in the single-letter codes. The COPI/COPII binding di-phenylalanine motifs of Emp24 and Erv25 are underlined, and the di-lysine motif of Rrt6 is double underlined. B, N-terminal epitope tagging of Rrt6. RRT6 gene was cloned into a low-copy plasmid, tagged with a 3×HA epitope at three different positions, and expressed in rrt6Δ cells. The bottom shows the predicted N-terminal sequence of Rrt6 with the tag insertion sites indicated by closed triangles. The open triangle indicates the predicted signal cleavage site. The tagged (*) and untagged (**) Rrt6 were detected by Western blot analysis using anti-HA or anti-Rrt6 antibodies. Lane 0, untagged Rrt6, Lanes 1–3, 3HA-Rrt6 variants. The lane numbers correspond to those in the bottom sequence. C, extraction of Rrt6 from the membrane. Whole-cell extract was adjusted to either 0.5 m NaCl (NaCl), 0.1 m sodium carbonate, pH 11, or 1% (w/v) Triton X-100 (TX-100), incubated at 4 °C for 30 min, and centrifuged at 100,000 × g for 1 h. The amounts of Rrt6, Erv25, and Vma22 in the pellet (P) and the supernatant (S) fractions were determined by Western blot analysis. Asterisk indicates an unrelated cross-reacting protein. D, N-glycosylation of Rrt6. Crude membrane fractions prepared from rrt6Δ cells expressing plasmid-borne RRT6 or rrt6-N96D were treated with recombinant endoglycosidase H (EndoH) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Wild-type and the N96D mutant Rrt6 were detected by Western blot analysis. The asterisk indicates an unrelated cross-reacting protein. E, limited trypsin digestion of Rrt6 in the membrane. A crude membrane fraction prepared from the cells expressing 3myc-Rrt6 was treated with trypsin at the concentrations indicated in the figure. The reaction was done at 37 °C for 30 min in the presence or absence of 0.1% (w/v) Triton X-100. Residual amounts of 3myc-Rrt6, Erv25, and Sec22 were determined by Western blot analysis. Anti-Erv25 antibodies recognize the luminal domain of the protein. 3myc-Rrt6 was probed with anti-myc and anti-Rrt6 C-tail (anti-Ct) antibodies.
