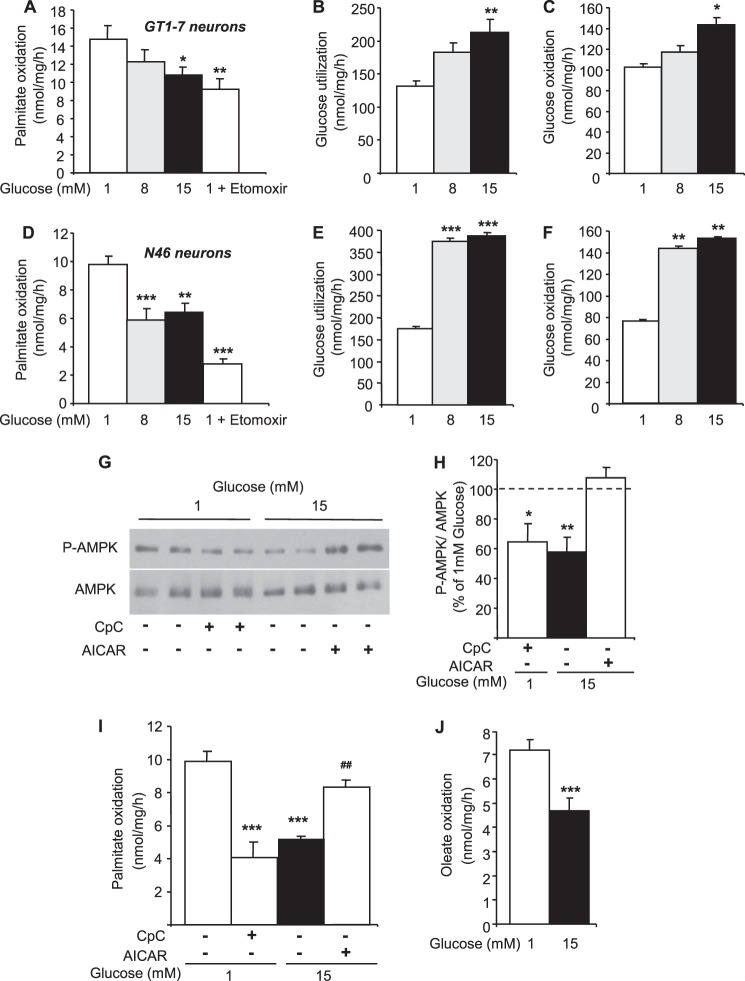
FIGURE 2.
Glucose inhibits LCFA oxidation via AMPK in hypothalamic neuronal cell lines. Palmitate oxidation (A), glucose utilization (B), and oxidation (C) in response to increasing glucose concentrations or etomoxir (200 μm) in GT1-7 neurons is shown. Palmitate oxidation (D), glucose utilization (E), and oxidation (F) in response to increasing glucose concentrations or etomoxir (200 μm) in N46 neurons is shown. Western blot (G), quantitation of Thr-172 phospho-AMPK levels (H), and palmitate oxidation (I) in N46 neurons treated with glucose with or without CpC (25 μm) or AICAR (1 mm) is shown. Oleate oxidation (J) in response to glucose in N46 neurons is shown. Results are shown as the means ± S.E. n = 3–6 independent experiments with each condition performed in duplicate for intracellular metabolism measurements. n = 3–4 independent experiments for Western blot analyses. Statistical analyses were performed with one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests except for oleate oxidation (unpaired Student's t test). *, **, and ***, p < 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively versus 1 mm glucose. ##, p < 0.01 versus 15 mm glucose.