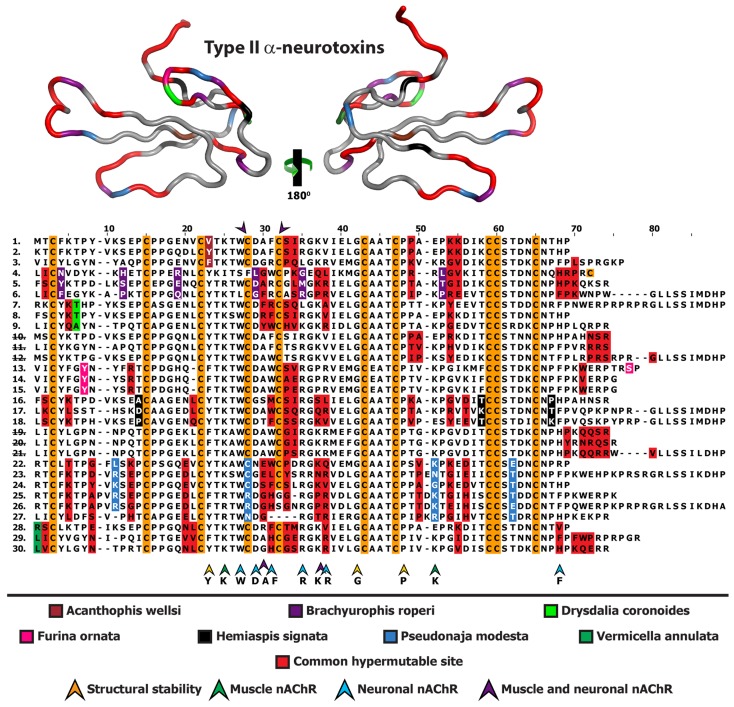
Figure 4.
Homology model depicting the locations of positively selected sites from various species, indicated by different colour codes. Multiple sequence alignment of Type II α-ntxs depicting the locations of positively selected sites is also presented. Representative sequences are from Acanthophis wellsi (1. GAGZ01000001, 2. GAGZ01000004, 3. GAGZ01000006), Brachyurophis roperi (4. GAHA01000003, 5. GAHA01000001, 6. GAHA01000002), Drysdalia coronoides (7. FJ481928, 8. FJ752461, 9. FJ752459), Echiopsis curta (10. GAHD01000001, 11. GAHD01000004, 12. GAHD01000006), Furina ornata (13. GAHE01000001, 14. GAHE01000009, 15. GAHE01000014), Hemiaspis signata (16. GAHF01000001, 17. GAHF01000005, 18. GAHF01000006), Suta fasciata (19. GAHI01000001, 20. GAHI01000004), 21. Parasuta nigriceps FJ790457, Pseudonaja modesta (22. GAHH01000040, 23. GAHH01000045, 24. GAHH01000046, 25. GAHH01000043, 26. GAHH01000042, 27. GAHH01000035) and Vermicella annulata (28. GAHJ01000009, 29. GAHJ01000010, 30. GAHJ01000016). Numerical IDs representing species lacking unique mutations are indicated by strikethrough.