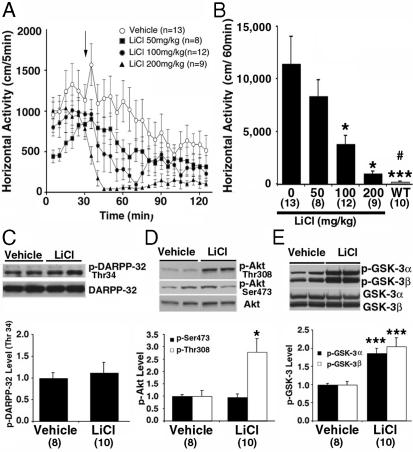
Fig. 1.
Lithium antagonizes behavioral responses to DA in DAT-KO mice. (A) DAT-KO mice were placed in a locomotor activity monitor for an initial period of 30 min and were then injected (arrow) with vehicle (saline) or with LiCl (50, 100, or 200 mg/kg of body weight i.p.). Horizontal activity was recorded every 5 min for a 2-h period. (B) Horizontal activity was quantified for a period of 1 h after injection of either vehicle or different doses of LiCl. Note that LiCl-treated DAT-KO mice remained more active than vehicle-treated WT mice observed under the same conditions. (C-E) Densitometric Western blot analysis of phosphoprotein relative levels in extract prepared from the striatum of DAT-KO mice 30 min after injection of LiCl (200 mg/kg of body weight i.p.) or vehicle. Antibodies directed against p-Thr-34-DARPP-32 (C), p-Thr-308-Akt (open bar in D), and p-Ser-473-Akt (filled bar in D) and with an antibody recognizing both p-GSK-3α (Ser-21, filled bar in E) and β (Ser-9, open bars in E) were used. Phospho-independent antibodies directed against these different proteins were used as loading controls for densitometry. For all results, data are means ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.001 as compared with vehicle-treated DAT-KO mice; #, P < 0.05 as compared with DAT-KO mice treated with 200 mg/kg LiCl. Numbers of animals per group (n) are indicated.