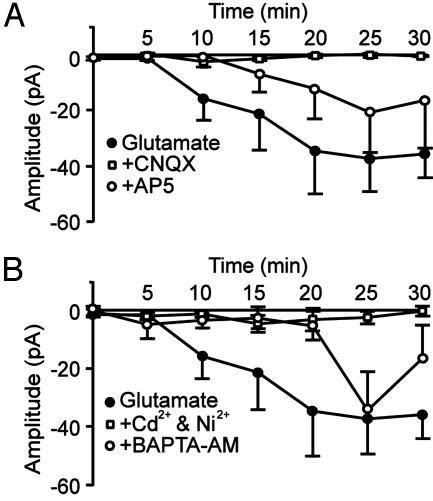
Fig. 4.
AMPA receptor activation and a rise in [Ca2+]i are required for the glutamate-induced increase in Ih. (A) Time course of the amplitude of Ih, recorded at a relative membrane potential of -60 mV during application of 100 μM glutamate (filled circles). In the continuous presence of 50 μM CNQX (open squares), the glutamate-induced increase in Ih was absent, whereas in the continuous presence of 100 μM d(-)-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (AP5, open circles), the increase in Ih was reduced and its onset delayed. (B) The continuous presence of 100 μMNi2+ and 100 μMCd2+ (open squares) prevented the increase in Ih. The effect of glutamate on Ih was prevented for up to 20 min after the start of glutamate application by loading the cells with 50 μM BAPTA-AM to buffer intracellular Ca2+(open circles). Data points represent mean ± SEM of four to seven cells.