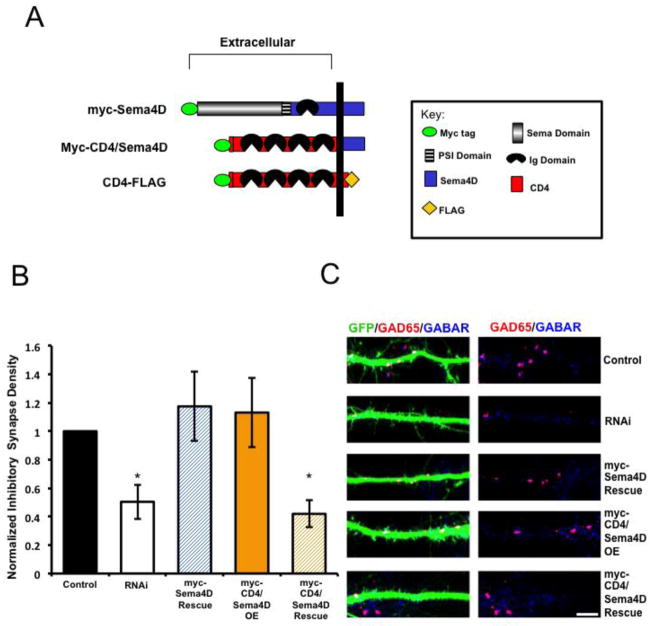
Figure 2. The extracellular domain of Sema4D is required for GABAergic synapse formation.
(a) Diagram illustrating the pertinent epitope-tagged Sema4D and CD4 chimeric constructs used in these experiments.
(b) Quantification of inhibitory GABAergic synapse density at DIV14 as defined by overlapping GAD65/GABARγ2 puncta onto hippocampal neurons transfected with either an empty vector (“Control,” n= 21 neurons), an shRNA targeting Sema4D (“RNAi,” n= 19 neurons), co-transfection of a myc-Sema4D RNAi resistant cDNA along with an shRNA targeting Sema4D (“myc-Sema4D Rescue,” n= 19 neurons), overexpression of a myc-tagged CD4/Sema4D RNAi resistant cDNA alone (“myc-CD4/Sema4D OE,” n=16 neurons), or co-transfection of the myc-CD4/Sema4D RNAi resistant cDNA along with an shRNA targeting Sema4D (“myc-CD4/Sema4D Rescue,” n=29 neurons). Asterisk indicates p<0.05 using a univariate ANOVA compared to myc-Sema4D rescue condition and control; Other pertinent p values include: p=0.777 for Control vs. myc-Sema4D Rescue and p=0.700 RNAi vs. myc-CD4/Sema4D Rescue. Error bars denote standard error (SEM).
(c) (Left) Immunostaining against GAD65 (red) and GABARγ2 (blue) proteins on a stretch of GFP-positive dendrite from a representative neuron transfected with the constructs indicated on far right; overlapping puncta onto the transfected neuron appear white. (Right) GAD65 and GABARγ2 immunostaining in the absence of the GFP signal; overlapping puncta appear magenta. Scale bar =5um.