FIGURE 1:
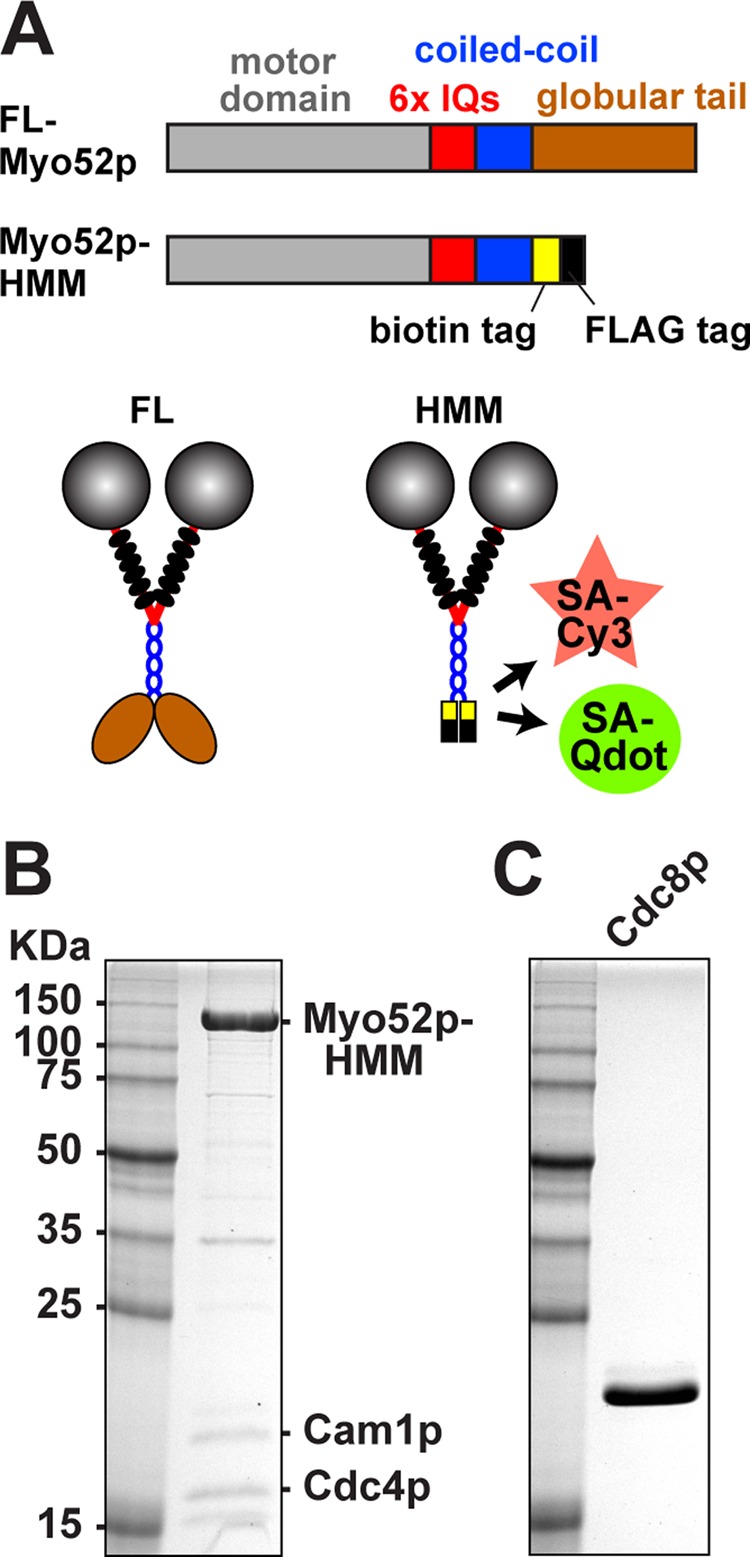
Myo52p constructs and purification. (A) Top, linear representations of full-length and truncated Myo52p constructs. The positions of specific domains are indicated on the full-length construct. Truncated Myo52p-HMM (amino acids 1–1056 of the Myo52p heavy chain) was used in TIRF-based motility assays. This construct contains a biotin tag following the coiled-coil for attachment to streptavidin-coated Qdots or streptavidin-Cy3, and a FLAG tag to facilitate affinity purification. The C-terminus of both full-length and truncated forms of Myo52p were fused to triple GFP for in vivo studies (Figures 4–6). Bottom, corresponding illustrations of double-headed Myo52p molecules. Six light chains (black ovals) bind to the IQ region of each Myo52p polypeptide. (B, C) Purified protein samples after SDS–PAGE and gel staining with Coomassie blue. Molecular weight standards are included in the left lanes. (B) Myo52p-HMM after elution from anti-FLAG purification resin. HMM was co-overexpressed with its two (untagged) light chains: Cam1p and Cdc4p. These light chains were also purified independently (see Materials and Methods) and added to HMM samples at 10-fold molar excess to minimize light-chain dissociation and suboptimal Myo52p motor activity in biochemical assays. (C) Fission yeast tropomyosin Cdc8p was purified from bacteria as an acetylated-mimicking form.
