FIGURE 7:
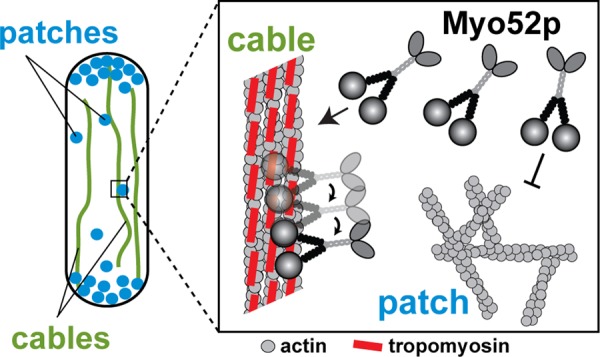
Sorting of Myo52p to actin cables during interphase. An interphase cell uses two distinct actin structures: 1) endocytic actin patches (blue) made up of branched actin filament networks that associate with myosin-I (Myo1p) and lack tropomyosin (Cdc8p), and 2) actin cables (green) made up of unbranched polarized Cdc8p-decorated actin filaments that support Myo52p transport throughout the cell cycle (Kovar et al., 2011). Box, the presence of Cdc8p on actin cables facilitates Myo52p interactions by converting cytoplasmic Myo52p molecules into processive motors, which preferentially bind to and move efficiently along the cables. The absence of tropomyosin at actin patches fails to support Myo52p processivity, preventing inappropriate interactions between myosin-V and endocytic actin structures.
