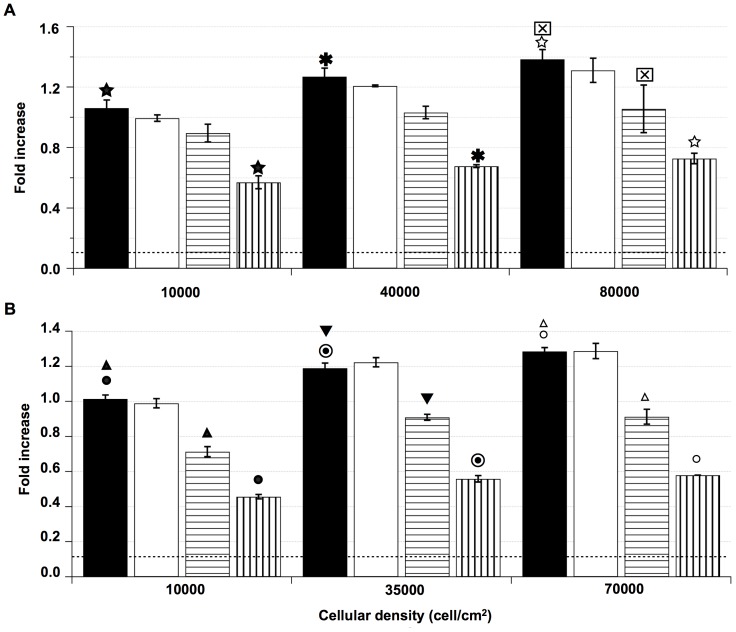
Figure 5. Cellular density effect on the cytoskeleton contribution to E-[c(RGDfK)2] and iRGD internalization.
U87 cells were incubated with E-[c(RGDfK)2] at different densities (10000; 40000; 80000 cell/cm2) (A) or with iRGD (10000; 35000; 70000 cell/cm2) (B). These densities were defined as low, medium and high density, respectively. Incubations were performed without inhibitor (▪), with paclitaxel (□), with cytoD ( ) or with colchicine (
) or with colchicine ( ). Results with paclitaxel were not significantly different. The cytoD effect on the E-[c(RGDfK)2] internalization was not significant at low density (15.65%±1.3%) but appeared significant for the highest density (23.9%±7.9%). For iRGD, significant results were observed for all the densities when cells were treated with cytoD (29.7%±1.3%; 23.5%±1.3%; 29.0%±2.1% at low, medium and high density, respectively). Treatment with colchicine induced a strong decrease of E-[c(RGDfK)2] and iRGD uptakes. For E-[c(RGDfK)2] the uptake results were 46.3%±1.3%, 46.6±3.0, and 47.5%±3.0% at low, medium and high density, respectively. iRGD uptake results were of 55.0%±0.3%, 53.1%±0.1% and 54.8%±0.8% at low, medium and high density, respectively. For these experiments (n≥3), the results (
). Results with paclitaxel were not significantly different. The cytoD effect on the E-[c(RGDfK)2] internalization was not significant at low density (15.65%±1.3%) but appeared significant for the highest density (23.9%±7.9%). For iRGD, significant results were observed for all the densities when cells were treated with cytoD (29.7%±1.3%; 23.5%±1.3%; 29.0%±2.1% at low, medium and high density, respectively). Treatment with colchicine induced a strong decrease of E-[c(RGDfK)2] and iRGD uptakes. For E-[c(RGDfK)2] the uptake results were 46.3%±1.3%, 46.6±3.0, and 47.5%±3.0% at low, medium and high density, respectively. iRGD uptake results were of 55.0%±0.3%, 53.1%±0.1% and 54.8%±0.8% at low, medium and high density, respectively. For these experiments (n≥3), the results ( ) and (★,
) and (★, ,☆,
,☆,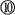 ,▾,▵,•,
,▾,▵,•, ,○) were significantly different with p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively.
,○) were significantly different with p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively.