Figure 5. Y. pseudotuberculosis Ail and the Y. pestis Ail single mutants have defects in HEp-2 cell adhesion and invasion relative to Y. pestis Ail, when expressed in Y. pestis.
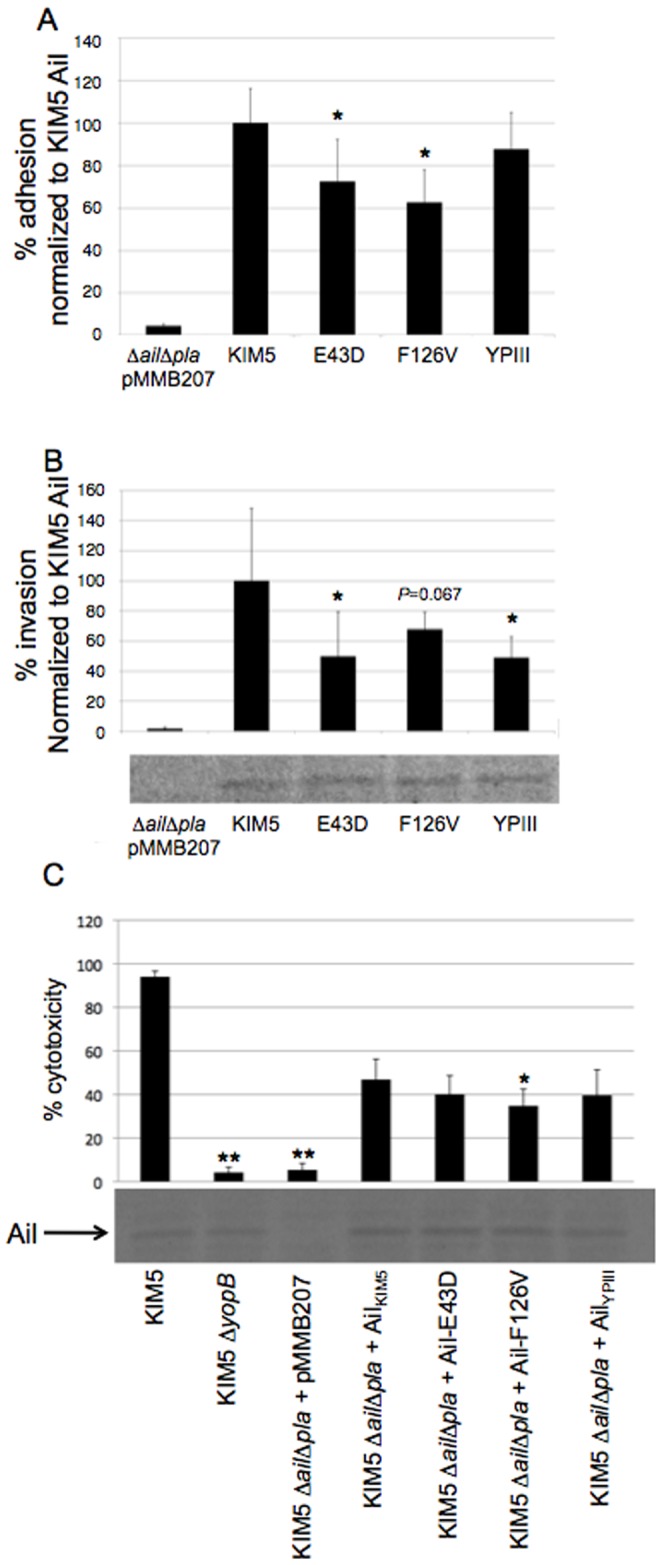
A) When expressed in the KIM5 ΔailΔpla strain, Ail-E43D and Ail-F126V have significantly lower levels of cell adhesion to HEp2-cells than KIM5 Ail; MOI = 50 bacteria/cell. Actual adhesion by Y. pestis Ail was ∼6%, n = 6. B) Levels of HEp-2 cell invasion by KIM5 ΔailΔpla expressing Ail-E43D, Ail-F126V and YPIII Ail, were also less than that by KIM5 Ail, although the Ail-F126V result had a P value of 0.067, rather than 0.05, MOI = 50. Invasion refers to the number of Y. pestis surviving gentamicin treatment for 1 hr after a 2 hour infection of cells, compared to the bacterial inoculum over the same time period on HEp-2 cells, n = 9. Ail expression levels were assessed by Coomassie gel staining. Actual invasion by Y. pestis Ail was ∼1.0%. C) HEp-2 cells were infected with KIM5 ΔailΔpla expressing the various Ail derivatives at an MOI of 10, to determine Ail-mediated cytotoxicity. After 4 hours of infection, cells were fixed and stained with Geimsa to show shrunken, round, darker cells, indicative of Yop-mediated cytotoxicity. Cells were counted and the percent of cytotoxic cells were calculated, n = 12. Again, Ail expression was assessed by Coomassie gel staining. *P<0.05, **P<10−11.
