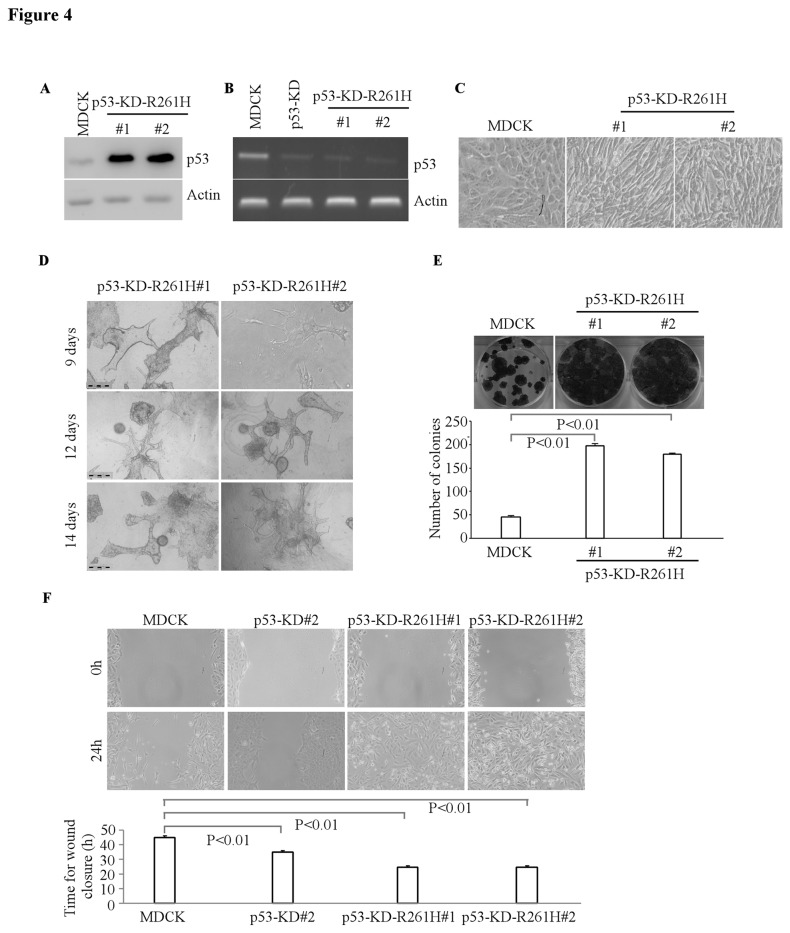
Figure 4. Ectopic expression of mutant p53 R261H cooperates with p53-KD to alter cyst morphology.
A, Generation of MDCK cell lines in which siRNA-resistant mutant p53 R261H was expressed along with knockdown of endogenous wild-type p53. The levels of wide-type p53 and mutant p53 R261H were determined by Western blotting. B, The level of wild-type p53 transcripts was determined by RT-PCR. C, Representative images of MDCK cells or MDCK cells with p53-KD-(R261H) in 2-D culture. D, Representative images of MDCK cells with p53-KD-R261H in 3-D culture for 12 d. Scale bar: 100 µM. E, Top panel: colony formation assay was performed with MDCK cells or MDCK cells with p53-KD-R261H. Bottom panel: the number of colonies was counted and presented as Mean ± SD from three separate experiments. F, Wound healing assay was performed with MDCK cells, MDCK cells with p53-KD, or MDCK cells with p53-KD-R261H. Top panel: cell migration was determined by visual assessment of cells migrating into the wound for 24 h using a phase-contrast microscopy. Bottom panel: the time required for wound closure was measured and presented as mean ± SD from three separate experiments.