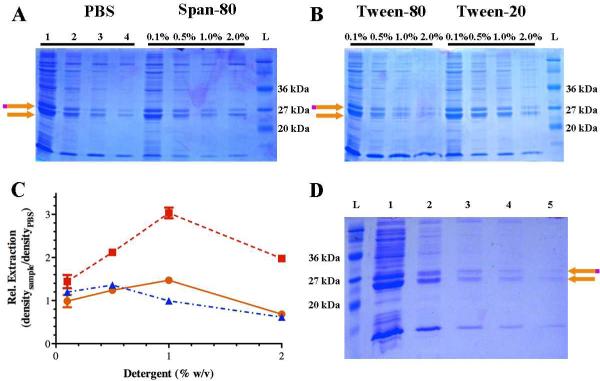
Figure 3. Extraction of GST-6xHis-melittin from the insoluble protein fraction.
Representative SDS-PAGE electrophoresis gels are shown to represent the protein recovered from extraction from the insoluble protein fraction. (A) Protein recovered from repeated extraction of the same insoluble fraction pellet with PBS (lanes 1-4 indicated the first through fourth PBS extraction) or sequential extraction of the same insoluble fraction pellet with 0.1% Span-80 followed by 0.5%, 1%, and finally 2% Span-80. (B) Protein recovered sequential extraction of the insoluble fraction with 0.1% Tween-90 or Tween-20 followed by 0.5%, 1%, and finally 2% Tween-80 or Tween-20. (C) Semi-quantitative density of extracted GST-6xHis melittin using Tween-80 ( ), Tween-20 (
), Tween-20 ( ), or Span-80 (
), or Span-80 ( ) relative to PBS extraction where the density of the protein band is divided by the density of the protein band from the serial PBS extraction. Three technical replicates were examined and the mean plus or minus (±) the standard deviation is presented. (D) Repeated extraction of same insoluble pellet using 1% Tween-20 where each lane indicates the order of extraction. The orange and magenta arrow indicates GST-6xHis-melittin and the orange arrow indicates GST-6xHis. A molecular weight ladder (L) is also included in each gel. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
) relative to PBS extraction where the density of the protein band is divided by the density of the protein band from the serial PBS extraction. Three technical replicates were examined and the mean plus or minus (±) the standard deviation is presented. (D) Repeated extraction of same insoluble pellet using 1% Tween-20 where each lane indicates the order of extraction. The orange and magenta arrow indicates GST-6xHis-melittin and the orange arrow indicates GST-6xHis. A molecular weight ladder (L) is also included in each gel. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)