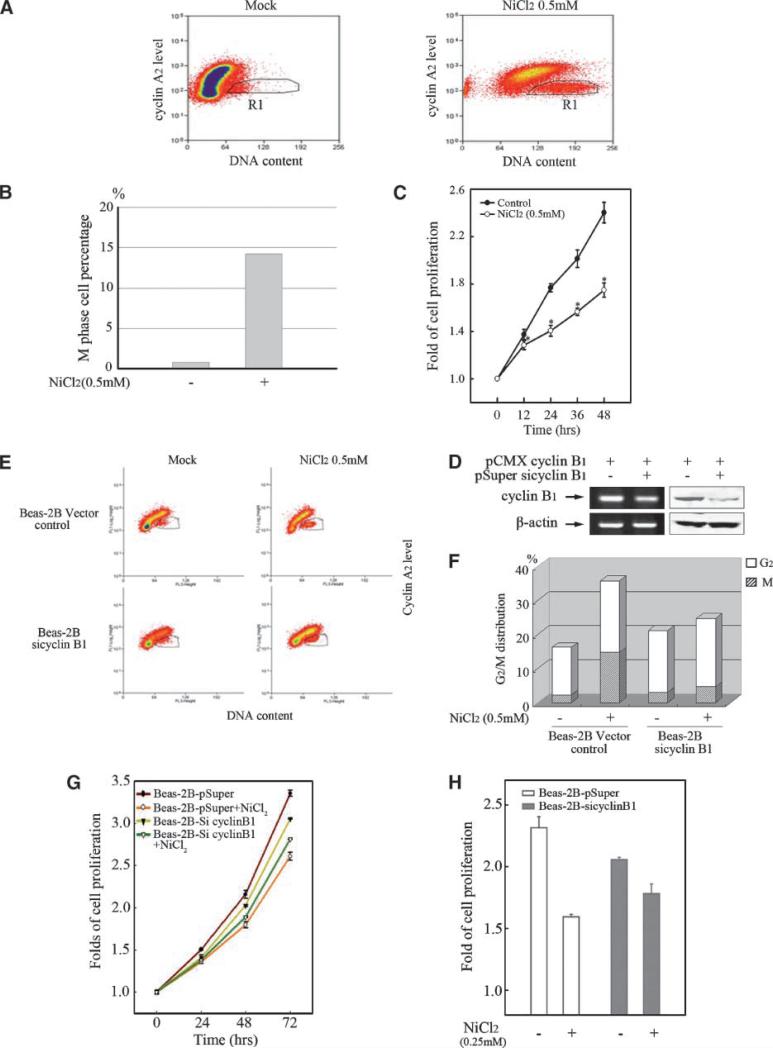
Figure 6.
Cyclin B1 is responsible for the nickel-induced M-phase arrest and cell growth inhibition. Beas-2B cells (A, B) were seeded into each well of 6-well plates and cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS until the cell density reached 70% to 80%. After the treatment of 0.5 mmol/L NiCl2 for 48 h, the cells were stained with propidium iodide and then incubated with 10 μL FITC-conjugated anti-cyclin A2. M-phase cell population was sorted by flow cytometry as described in Materials and Methods. D. Beas-2B cells were transiently transfected with pCMX cyclin B1 expression plasmid together with pSuper/sicylin B1 or Vector control respectively using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent. RT-PCR and Western blot were carried out as described above. Beas-2B cells transiently transfected by pSuper/siCyclin B1 or vector control (E, F) were seeded respectively into each well of 6-well plates and cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS. After the cell density reached 70% to 80%, the cells were exposed to 0.5 mmol/L NiCl2 for 48 h. Cell cycle distribution was determined by flow cytometry as described above. Every result was from one representative of three independent experiments. 1 × 103 of Beas-2B cells (C) or Beas-2B cells transiently transfected by pSuper/siCyclin B1 or vector control (G and H) were seeded into each well of 96-well plates, cultured in 10% FBS DMEM overnight, and then exposed to 0.5 mmol/L (C) or 0.25 mmol/L (G) NiCl2 for various time periods. The cell proliferation was evaluated as described in Materials and Methods. The comparison of cell growth between the Beas-2B cells transiently transfected by pSuper/siCyclin B1 and vector control was presented (H). Each result was presented as an arithmetical average of three independent assays.