Figure 1.
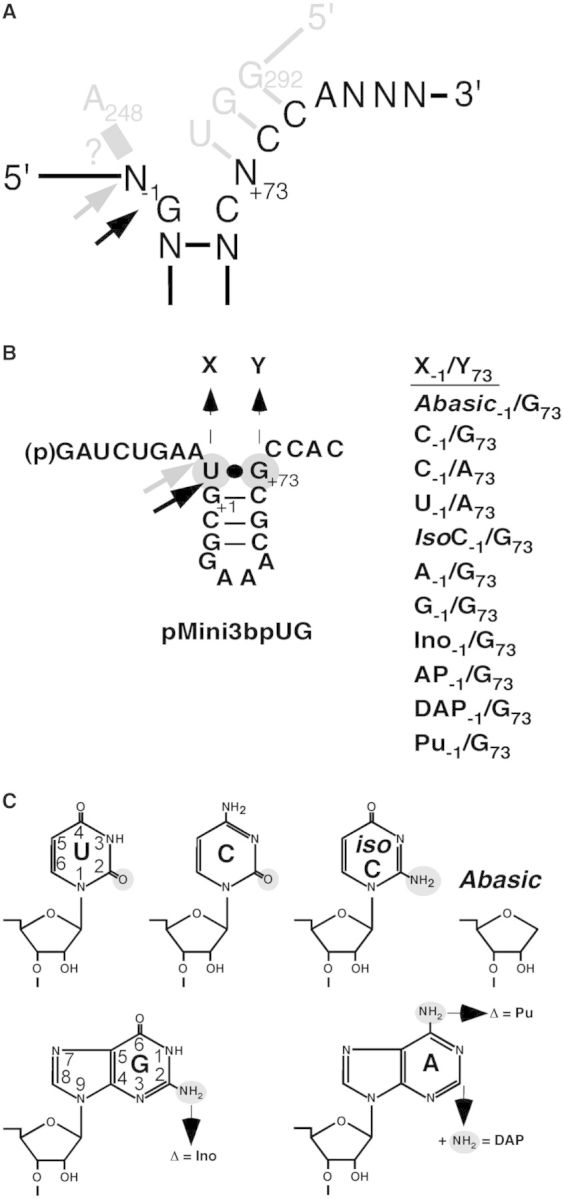
Structures of the model hairpin loop substrate pMini3bp and structure of uridine, cytidine, iso-cytidine, guanosine and adenosine. (A) Illustration of the N−1/248 - and the RCCA-RPR interactions [interacting residues underlined (6,9,10)]. Substrate residues are marked in black and residues marked in grey represent the RPR. Black and grey arrows mark the canonical and the alternative cleavage sites, respectively. ? indicate if and how residues −1 and 248 interact (see the main text). (B) Structure of pMini3bpUG and its derivatives. The black arrow marks the canonical cleavage site at +1 and the grey arrow marks the alternative cleavage site −1. X and Y indicate where base changes were introduced as indicated on the right side. Abasic, deletion of the base; IsoC, iso-cytidine; Ino, inosine; 2AP, 2-amino purine; DAP, 2;6-diamino purine; Pu, purine. (C) Structure of the bases uridine (U), cytidine (C), iso-cytidine (IsoC), Abasic, guanosine (G) and adenosine (A). Chemical groups marked in small grey circles refer to the groups that were substituted or deleted as indicated. The ring numbering for U and G is as indicated. For details see text.
