Figure 3.
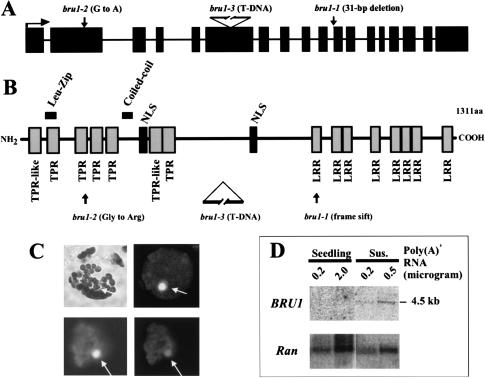
The BRU1 gene encodes a novel nuclear protein. (A) Structure of the BRU1 gene and its mutant alleles (exons are marked as black rectangles, introns as lines, and translation start as horizontal arrow). Positions of mutations are indicated. (B) Structure of the BRU1 protein. Predicted functional motifs and positions of mutations are indicated. (C) Nuclear localization of BRU1–GFP fusion protein, showing a bright-field image of a transformed proto-plast (top left) and a dark-field image of GFP fluorescence (top right, no Triton X-100 treatment). Below images of DAPI-stained nuclei (bottom left) and GFP fluorescence (bottom right) in the presence of Triton X-100. Nuclei are indicated by arrows. (D) Northern blot analysis of BRU1 mRNA. Lanes with poly(A)+ RNA from seedlings and suspension culture cells (Sus.) are marked. RNA was hybridized with probes for BRU1 and AtRanBP1a (Ran; Haizel et al. 1997) as a loading control.