Figure 1.
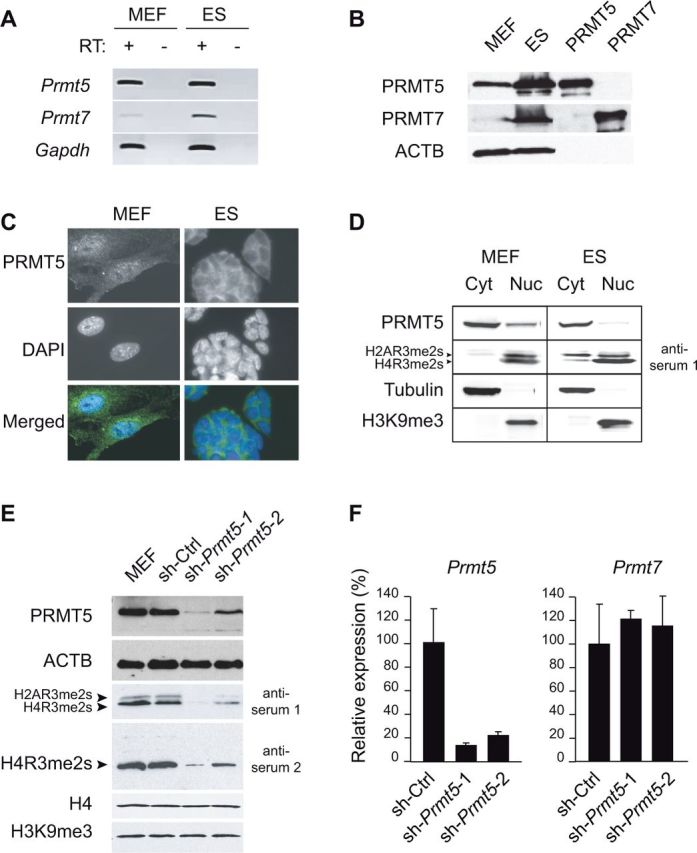
PRMT5 expression, localization and histone methylation activity in embryonic cells. (A) RT-PCR analysis of Prmt5 and Prmt7 expression in primary MEFs and ES cells. RT+ and RT– indicate presence and absence of reverse transcriptase (RT), respectively. (B) Western blot analysis of total protein extracts. Lanes ‘PRMT5’ and ‘PRMT7’ were loaded with diluted protein samples of 293T cells in which the PRMT5 and PRMT7 proteins were over-expressed. β-Actin (ACTB) is used as a loading control. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of PRMT5 in MEFs and ES cells (upper panels). Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI (middle panels). (D) Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic (Cyt) and nuclear (Nuc) protein fractions of MEFs and ES cells. Tubulin and H3K9me3 constitute cytoplasmic and nuclear controls, respectively. (E) Strongly reduced PRMT5 protein expression in MEFs stably infected with lentiviral shRNA constructs (sh-Prmt5-1 and sh-Prmt5-2) directed against Prmt5. As a negative control, MEFs stably expressing a scrambled shRNA (Sh-Ctrl) were analysed. PRMT5, H4R3me2s (anti-serum 2) and H2A/H4R3me2s levels (anti-serum 1) were assessed by western blotting of total protein extracts; ACTB provides a loading control. (F) Strongly reduced Prmt5 gene expression in sh-Prmt5-1 and sh-Prmt5-2 cells. cDNA was made from total RNAs using random oligonucleotides. Expression levels were determined relative to Gapdh by real-time PCR amplification, and were put arbitrarily at 100% in the control cells (Sh-Ctrl).
