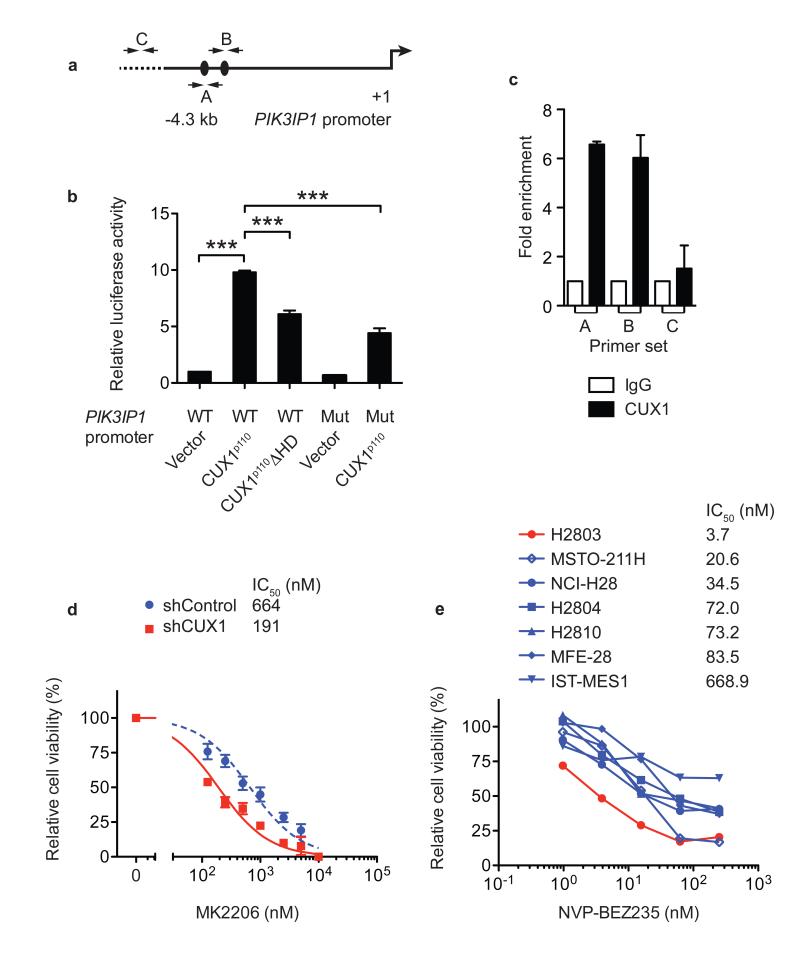
Figure 4. CUX1 directly regulates PIK3IP1 expression and CUX1 deficiency increases sensitivity to PI3K-AKT-mTOR inhibition.
(a) 4.3-kb genomic fragment upstream of PIK3IP1 transcriptional start site (+1) used for promoter luciferase assays. Black ovals, putative CUX1-binding sites (ATCAAT). A, B, C; primer-binding sites for qPCR in (c).
(b) Promoter luciferase assays in 293T cells using indicated PIK3IP1 promoter-luciferase constructs and CUX1 expression vectors. WT, wild-type; Mut, mutant; ΔHD, homeodomain-deletion mutant. Data were normalized to WT PIK3IP1 promoter + vector and represent mean + s.e.m. of 3 independent experiments assessed in triplicate. *** p < 0.001, t-test.
(c) ChIP-qPCR assays in LOUCY cells using indicated antibodies for regions shown in (a) (mean + s.e.m. of 3 independent experiments assessed in duplicate).
(d, e) Cell viability dose-response curves of KE37 shRNA vector-transduced cells (d) and human mesothelioma cell lines (e) treated with MK2206 or NVP-BEZ235. Data in (d) mean ± s.e.m. of triplicate experiments; (e) mean of duplicate experiments. IC50 for each cell line is shown.