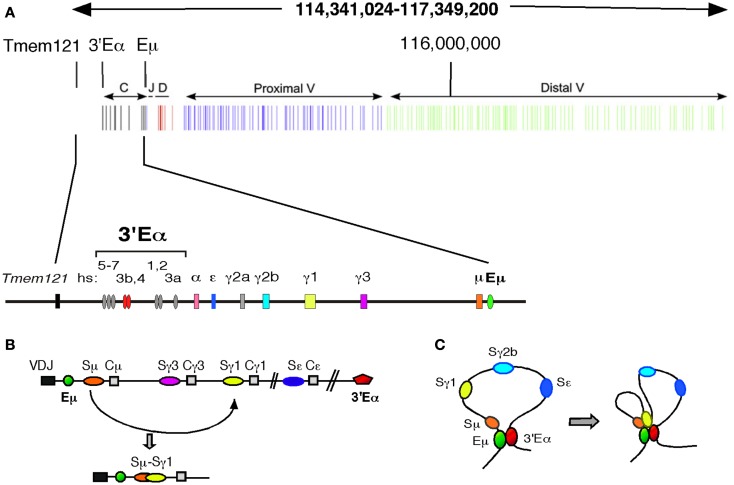
Figure 1.
Long range chromatin looping interactions in the Igh locus facilitate CSR in mature B cells. (A) A schematic map, drawn to scale of the 2.9 Mb Igh locus located on chromosome 12 (chr12: 114,341,024–117,349, 200 mm9). The CH, JH, DH, and proximal and distal VH gene segments are indicated. The Igh enhancers, 3′Eα and intronic Eμ bracket the CH region gene cluster (top). A schematic showing an expanded segment of the Igh locus spanning 220 kb and containing the CH region genes (bottom). The orientation of this map follows the chromosomal organization of the Igh locus. (B,C) Diagrams of the Igh CH locus describing CSR are by convention shown with the Eμ enhancer at the 5′ end. (B) CSR promotes diversification of CH effector function while retaining the original V(D)J rearrangement. Within the mouse Igh locus, a 220 kb genomic region contains eight CH genes (encoding μ, δ, γ3, γ1, γ2b, γ2a, ε, and α chains) each paired with repetitive switch (S) DNA (with the exception of Cδ). CSR is focused on S regions and involves an intra-chromosomal deletional rearrangement. Germline transcript (GLT) promoters, located upstream of I exon-S-CH regions, focus CSR to specific S regions by differential transcription activation (50, 67). Prior to CSR and upon GLT expression, S regions become accessible to AID attack. AID initiates a series of events culminating in formation of S region specific double strand breaks (DSBs) at the donor Sμ and a downstream acceptor S region (50). DNA DSBs in transcribed S regions are essential for CSR. Here, Sμ and Sγ1 acquire AID induced DSBs and engage in CSR to form recombinant Sμ/Sγ1 regions. (C) In mature B cells Eμ:3′Eα interactions create a long range chromatin loop encompassing the CH domain of the Igh locus (left). Upon B cell activation with LPS + IL4, long range chromatin interactions directed by the GLT promoters and Igh enhancers creates spatial proximity between Sμ and the downstream Sγ1 region locus (46). This spatial proximity facilitates recombination between the broken S regions and creates a matrix of chromatin contacts, which stabilize the locus during the recombination transaction.