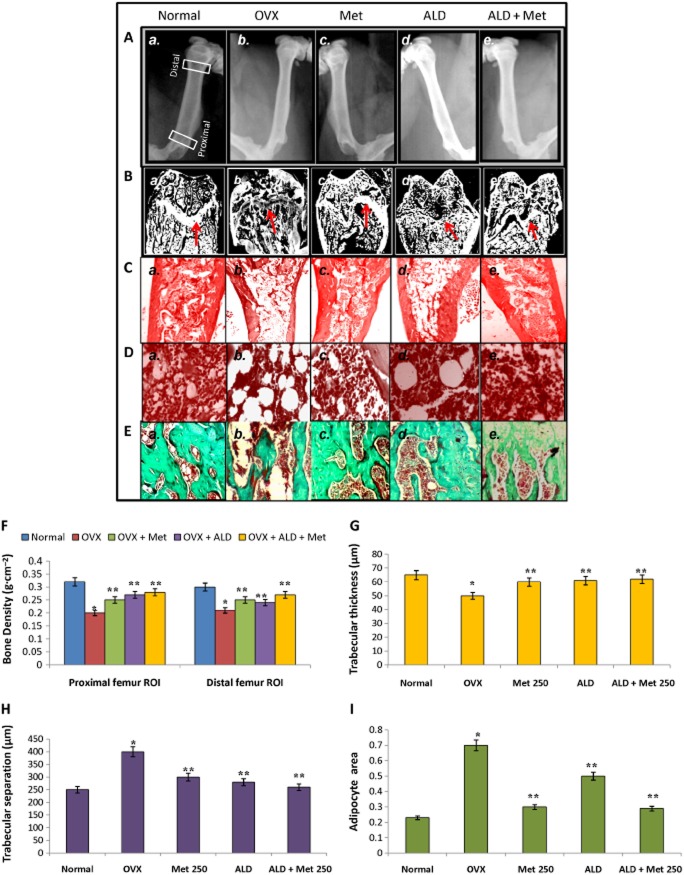
Figure 5.
Bone physiology of normal, OVX and treatment groups. Methionine at a dose of 250 mg·kg−1 body wt was administered in drinking water for 10 weeks. Alendronate (200 μg·kg−1 body wt) was administered p.o. to OVX rats at an interval of 5 days for 1 month. For combination therapy, rats were administered alendronate (100 μg·kg−1 body wt) and methionine (250 mg·kg−1 body wt). Both treatments were performed 6 h apart. (A) Radiographs of femur were acquired on Kodak FX Pro in the X-ray mode. Each animal received an approximate radiation dose of 1.4 Rad during imaging. (B) Images of femoral bone head of normal and experimental rats acquired using Image J after haematoxylin and eosin (H & E) staining. Red arrows indicate changes in growth plate. (C) H & E staining of femur showing changes in trabecular structure between normal and experimental rats. (D) H & E staining of femur showing changes in adipogenesis between normal and experimental rats. (E) Masson Trichome staining of femur showing changes in collagen level between normal and experimental rats. (F) Bone density measurements of femoral bone samples from normal and experimental rats. Bone density was measured and analysed by bone density software module employing a Carestream Molecular Imaging software version 5.0.7 (G–I) Changes in trabecular thickness, trabecular separations and adipogenesis in normal and experimental rats analysed using Bone J and Image J, Adipocyte area refers to area of bone marrow adipocytes in units of bone trabecula. Values are mean ± SEM; n = 4. *P < 0.05 compared with normal rat. **P < 0.05 compared with OVX rat.