Figure 3.
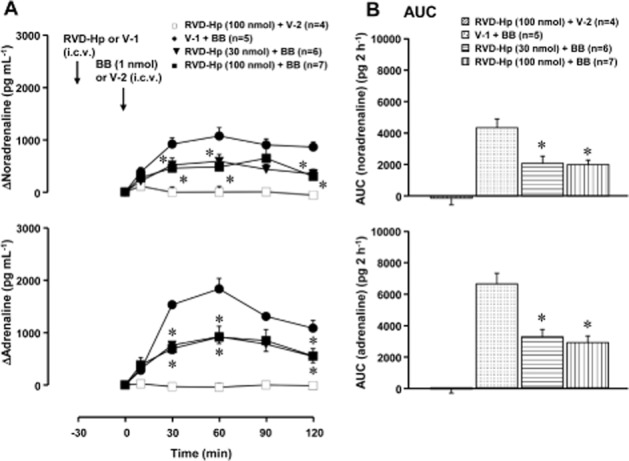
Effect of RVD-haemopressin (RVD-Hp) on the bombesin-induced elevation of plasma catecholamines. RVD-Hp (a peptide agonist of CB1 receptors; 30 or 100 nmol·per animal) or vehicle-1 (V-1; 10 μL saline·per animal) was given i.c.v. 30 min before the administration of bombesin (BB, 1 nmol·per animal, i.c.v.) or vehicle-2 (V-2; 10 μL saline·per animal, i.c.v.). (A) Increments of plasma catecholamines above the basal level. Arrows indicate the administration of RVD-Hp/V-1 and bombesin/V-2. The actual values for noradrenaline and adrenaline at 0 min were 289 ± 53 pg·mL−1 and 72 ± 10 pg·mL−1 in the V-1-pretreated group (n = 5), 494 ± 46 pg·mL−1 and 158 ± 31 pg·mL−1 in the RVD-Hp- (30 nmol·per animal) pretreated group (n = 6) and 600 ± 63 pg·mL−1 and 230 ± 53 pg·mL−1 in the RVD-Hp- (100 nmol·per animal) pretreated group (n = 11) respectively. (B) The AUC of the elevation of plasma catecholamines above the basal level for each group. *P < 0.05, significantly different from the V-1- and bombesin-treated group; ANOVA, with Bonferroni post hoc test. Other conditions are the same as those of Figure 1.
