Figure 1.
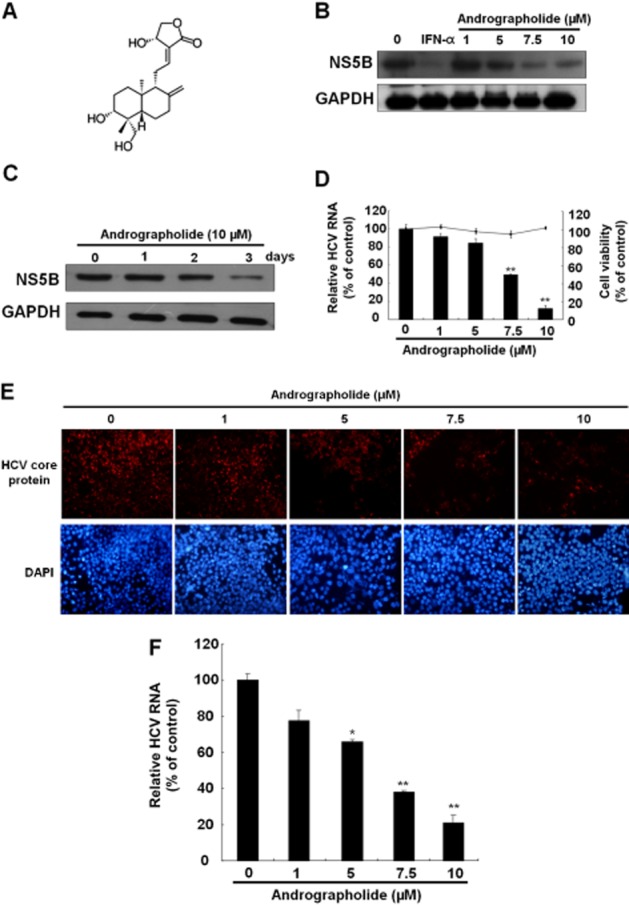
Andrographolide inhibits HCV replication. (A) Structure of andrographolide. The molecular formula is C20H30O5. (B, C) Reduction of HCV protein synthesis by andrographolide in a (B) concentration- and (C) time-dependent manner. Ava5 cells were treated with andrographolide at different concentrations (0–10 μM) for 3 days or for different time periods (1–3 days) with 10 μM andrographolide. IFN-α treatment served as a positive control. Protein synthesis was evaluated by Western blotting with anti-HCV NS5B antibody. Equal loading of cell lysates was confirmed by probing the same blot with anti-GAPDH antibody. (D) Reduction of HCV RNA replication by andrographolide in Ava5 cells. qRT-PCR was performed to quantify HCV RNA levels in the andrographolide-treated Ava5 cells after 3 days of incubation. The HCV RNA level was normalized against the cellular gapdh mRNA level and is presented as the percentage change relative to the andrographolide-untreated control. Cellular toxicity was evaluated by the MTS assay after incubation of cells with andrographolide for 3 days and is presented as the percentage change relative to the andrographolide-untreated control. (E, F) Concentration-dependent inhibition of HCVcc protein expression (E) and RNA replication (F) by andrographolide. The HCVcc-infected Huh-7 cells were treated with andrographolide at different concentrations (0–10 μM). On day 9 after infection, the HCV core-positive cells were detected by the immunofluorescence assay using anti-HCV core antibody. The total cells were visualized using DAPI nucleus stain. At 3 days after infection, HCV RNA levels and cell viability were assayed by qRT-PCR and MTS respectively. Results are represented as means ± SD (error bar) of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
