Figure 6.
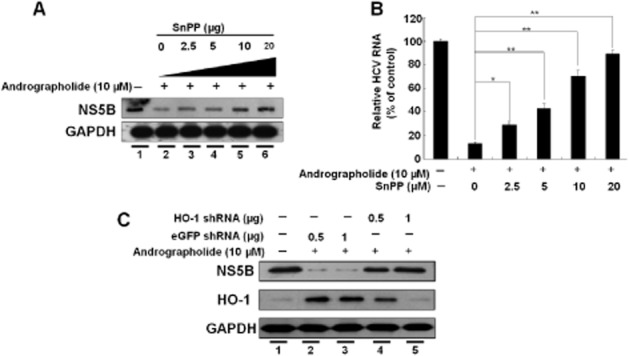
Inhibition of HO-1 expression attenuates the suppression of HCV replication by andrographolide. (A, B) Restoration of andrographolide-reduced HCV protein synthesis (A) and HCV RNA replication (B) by the HO-1-specific inhibitor SnPP. Ava5 cells were co-incubated with andrographolide (10 μM) and increasing concentrations of SnPP (0–20 μM) for 3 days. The cell lysates and total RNAs were subjected to Western blotting and qRT-PCR analysis respectively. The HCV RNA level was normalized against the cellular gapdh mRNA level and presented as the % change relative to andrographolide/SnPP-untreated cells (defined as 100%). (C) Restoration of andrographolide-reduced HCV protein synthesis by HO-1 gene knockdown. Ava5 cells were transfected with non-specific eGFP shRNA vectors or different amounts of the HO-1-specific shRNA (0.5 and 1.0 μg) for 12 h. The transfected cells were then treated with 10 μM andrographolide for 3 days. Protein synthesis was detected by Western blotting with anti-HCV NS5B or anti-HO-1 antibody. Equal loading of cell lysates was confirmed by probing the same blot with anti-GAPDH antibody. The experiments were performed in triplicate, and error bars indicate mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
