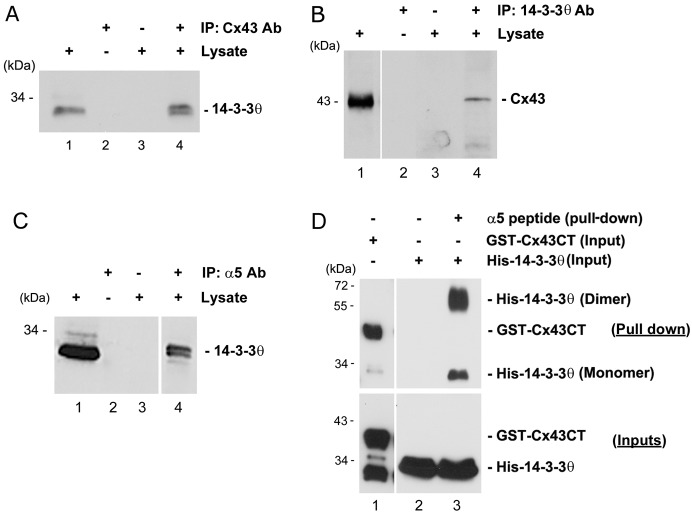
Fig. 1.
14-3-3θ interacts with Cx43 and integrin α5. (A) Lysates of MLO-Y4 cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-Cx43 antibody (lane 4). Cell lysates (lane 1) and immunoprecipitates (lanes 2–4) were immunoblotted with anti-14-3-3θ antibody. Beads incubated only with either 14-3-3θ antibody (lane 2) or lysates (lane 3) served as negative controls. (B) Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-14-3-3θ antibody (lane 4), and cell lysates (lane 1) and immunoprecipitates (lanes 2–4) were immunoblotted with anti-Cx43 antibody. Beads incubated only with either 14-3-3θ antibody (lane 2) or lysates (lane 3) served as negative controls. (C) Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-integrin α5 antibody (lane 4), and cell lysates (lane 1) and immunoprecipitates (lanes 2–4) were immunoblotted with anti-14-3-3θ antibody. Beads incubated only with integrin α5 antibody (lane 2) or lysates (lane 3) served as negative controls. (D) Purified GST–Cx43CT (lane 1) or His–14-3-3θ (lanes 2 and 3) was pulled down using a peptide containing the C-terminus of integrin α5 (α5 peptide) conjugated with magnetic beads. Pull down of His–14-3-3θ with magnetic beads alone served as negative control (lane 2). Elutes (upper panel) from the pull-down assay were immunoblotted with either anti-Cx43 antibody (lane 1) or anti-14-3-3θ antibody (lane 2 and 3). The inputs (lower panel) were immunoblotted with either GST (lane 1) or 14-3-3θ (lanes 2 and 3) antibody.