Fig. 1.
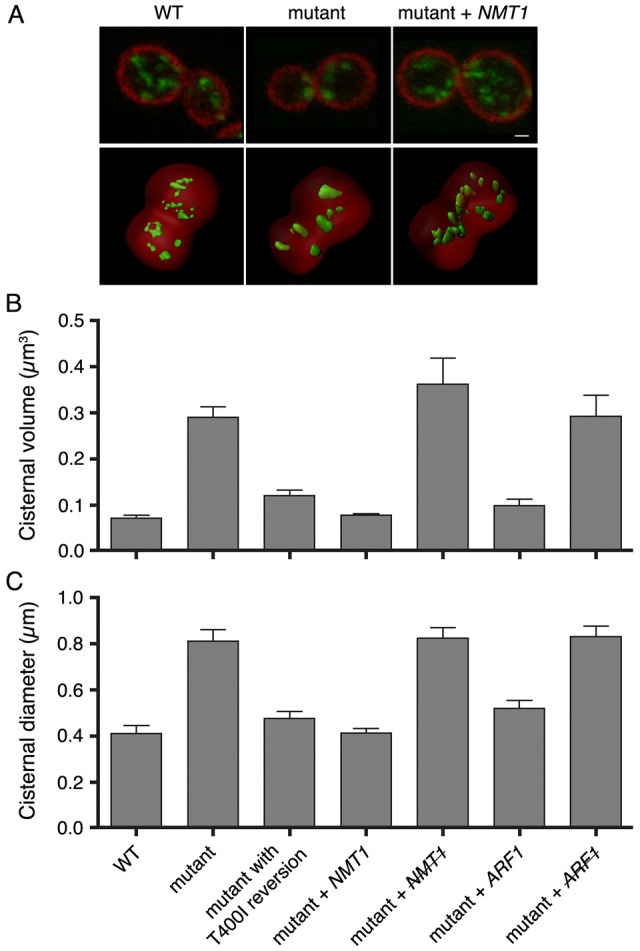
A conditional mutation in NMT1 generates enlarged late Golgi cisternae. (A) Representative images of the wild-type (WT) parental strain, the thermosensitive mutant, and the mutant transformed with a centromeric plasmid encoding NMT1. The plasma membrane was labeled with mCherry–Ras2 (red), and the late Golgi was labeled with Sec7–GFPx3 (green). The top row shows projected confocal sections of a central portion of the cell, and the bottom row shows 3D renderings. Scale bar: 1 µm. (B,C) Images of the type shown in A were quantified by rendering late Golgi cisternae as closed surfaces. The following strains were examined: the wild-type, the thermosensitive mutant, the mutant in which the nmt1 T400I mutation was reverted by gene replacement, the mutant transformed with a centromeric plasmid encoding NMT1, the mutant transformed with the plasmid encoding NMT1 and then cured of this plasmid (indicated by the strikethrough), the mutant transformed with a high copy number plasmid encoding ARF1, and the mutant transformed with the plasmid encoding ARF1 and then cured of this plasmid (indicated by the strikethrough). Sizes of the rendered late Golgi elements were quantified by measuring either (B) the average volume or (C) the average X–Y-plane diameter. Error bars indicate s.e.m.
