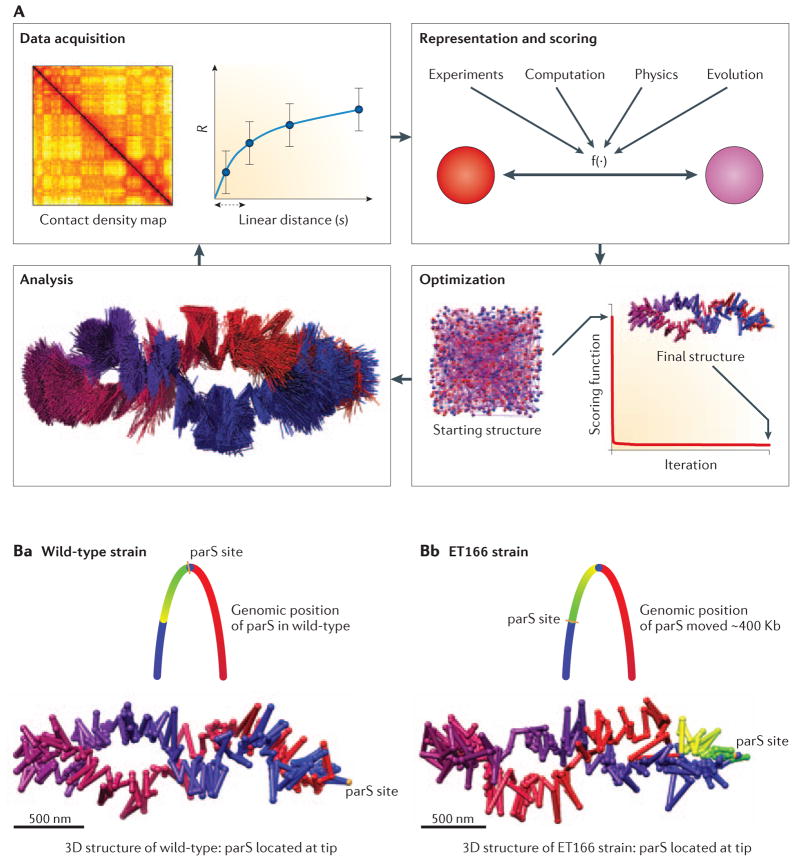
Figure 4. 3D modeling of genomes and genomic domains.
A. Iterative and integrative process for model building. The iterative process consists of data acquisition, model representation and scoring, model optimization, and model analysis. B. 3D model of the wild-type Caulobacter genome highlighting the position of the parS site located at the tip of the elliptical 3D structure of the genome. C. 3D model of the ET166 strain where the parS site has been moved ~400Kb of its original locus (indicated in the schematic diagram of the genome). In the 3D structure of genome of the ET166 strain the parS site are found at the tip of the structure again, which required a genome-wide rotation. The 3D models of Caulobacter are described in 72. Models in panels A, B and C are reproduced from 72, with permission.