Figure 1. Conformational Switch that Really Matters.
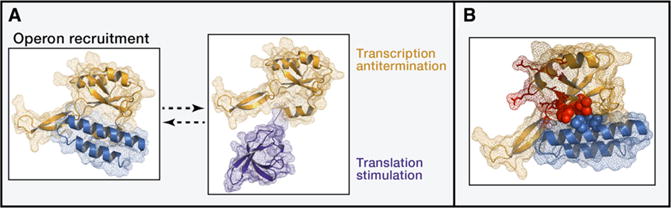
(A) Closed and open conformations of E. coli RfaH. (Left) Closed conformation (2oug,a; Belogurov et al., 2007). N-terminal (yellow) and C-terminal (blue) domains are mesh and cartoon. (Right) Homology model (adding 2lcl as a template) of the open conformation (Burmann et al., 2012). N- and C-terminal domains are mesh and cartoon.
(B) Part of the DNA-binding patch of the RfaH N-terminal domain is obscured by interactions with C-terminal domain in the closed conformation. E. coli RfaH (2oug,a) N- and C-terminal domains are mesh and cartoon; DNA-binding patch residues are red sticks (Tyr8, Cys9, Lys10, Gly12, Arg16, Pro52, Asn53, Thr72, and Val75) or red spheres (Leu6, Tyr54, and Val79). The last three are packed against C-terminal domain residues Leu143 and Ile146 (blue spheres).
