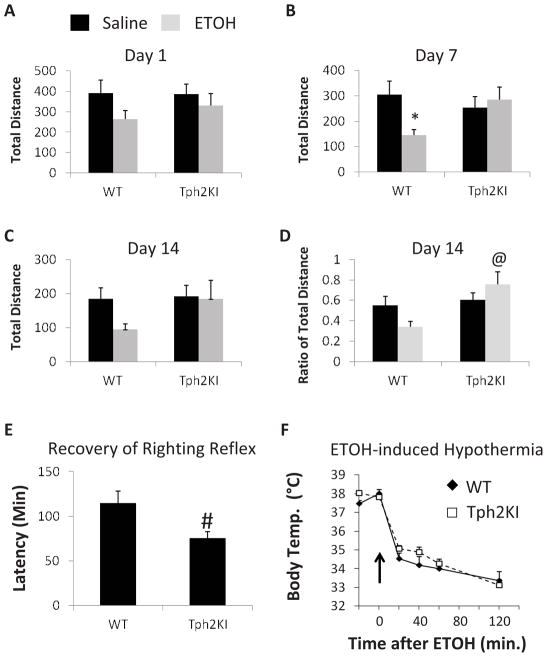
Figure 2.
The sedative and locomotor inhibitory effects of ETOH are reduced in Tph2KI mice. A single dose of ETOH did not have any significant effects on total distance travelled in either WT or Tph2KI mice (A). However, by the seventh day of repeated daily injections, ETOH significantly reduced the distance travelled in WT but not in Tph2KI animals (B). This effect on total distance was not quite significant on day 14 (C), but the ratio of the distance travelled in the 20 min following ETOH administration compared to the 20 min immediately before ETOH administration was higher in Tph2KI mice compared to WT controls (D). Tph2KI mice exhibit a more rapid recovery of righting reflex than WT animals (E). No genotype differences in ETOH-induced hypothermia were observed (F). N = 17–19 per group for A–D. N = 26 WTs and 24 Tph2KIs for E. N = 9 WTs and 8 Tph2KIs for F. * indicates p < 0.05 compared to WT saline, and @ indicates p < 0.05 compared to WT ETOH by Tukey’s post hoc test. # indicates p < 0.05 compared to WT by Student’s t test.