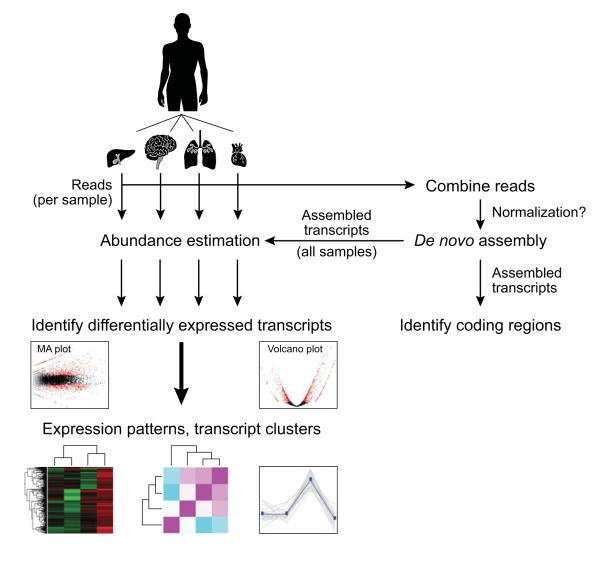
Figure 2. De novo transcriptome assembly and analysis workflow.
Reads from multiple samples (e.g., different tissues, top) are combined into a single data set. Reads may be optionally normalized to reduce read counts while retaining read diversity and sample complexity. The combined read set is assembled by Trinity to generate a ‘reference’ de novo transcriptome assembly (right). Protein coding regions can be extracted from the reference assembly using TransDecoder and further characterized according to likely functions based on sequence homology or domain content. Separately, sample-specific expression analysis is performed by aligning the original sample reads to the reference transcriptome assembly on a per sample basis, followed by abundance estimation using RSEM. Differentially expressed transcripts are identified by applying Bioconductor software, such as edgeR, to a matrix containing the RSEM abundance estimates (number of RNA-Seq fragments mapped to each transcript from each sample). Differentially expressed transcripts can then be further grouped according to their expression patterns.