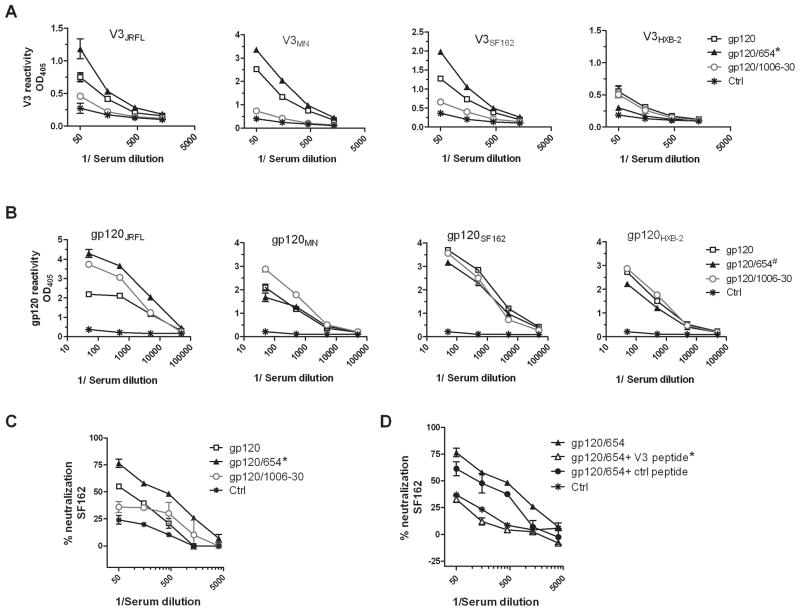
Figure 1. Comparison of Ab responses induced by immunization with gp120/654 (CD4bs) versus gp120/1006-30 (C2).
(A) BALB/c mice were immunized i.p. four times every two weeks with gp120JRFL alone or in complex with the anti-CD4bs mAb 654 or the anti-C2 mAb 1006-30. The complexes were prepared by incubating 3 μg gp120 and 9 μg mAb in 50 μl of PBS per animal and mixing them with adjuvant MPL/DDA. Sera were collected two weeks after the last immunization, pooled, diluted serially, and tested in ELISA for binding to V3 peptides from JRFL, MN, SF162, and HXB-2. Sera from control mice injected only with the adjuvant (ctrl) were tested in parallel. *, p<0.05 as compared to gp120/1006-30 and control. OD405, optical density at 405 nm. (B) Sera were also tested in ELISA for binding to recombinant gp120 proteins of JRFL, MN, SF162, and HXB-2. #, p<0.05 as compared to control, but not significantly different from gp120 and gp120/1006-30. (C) Virus-neutralizing activity was assessed against HIV-1 SF162 pseudovirus. Virus was incubated for 1 hr at 37°C with diluted sera and added to TZM-bl cells in the presence of diethylaminoethyl and indinavir. Virus infection was determined after 48 hrs using the Bright-Glo Luciferase Assay System (Promega, Madison, WI) *, p<0.05 as compared to gp120, gp120/1006-30, and control. (D) Sera from mice immunized with the gp120JRFL/654 complex were pre-treated with reactive V3 peptide or non-reactive control peptide (40 μg/ml), and tested for the capacity to neutralize SF162. *, p<0.05 as compared to untreated sera from gp120/654-immunized mice and sera treated with control peptide. Means and standard deviations from one representative experiment are shown. All experiments were repeated at least two times with consistent results.