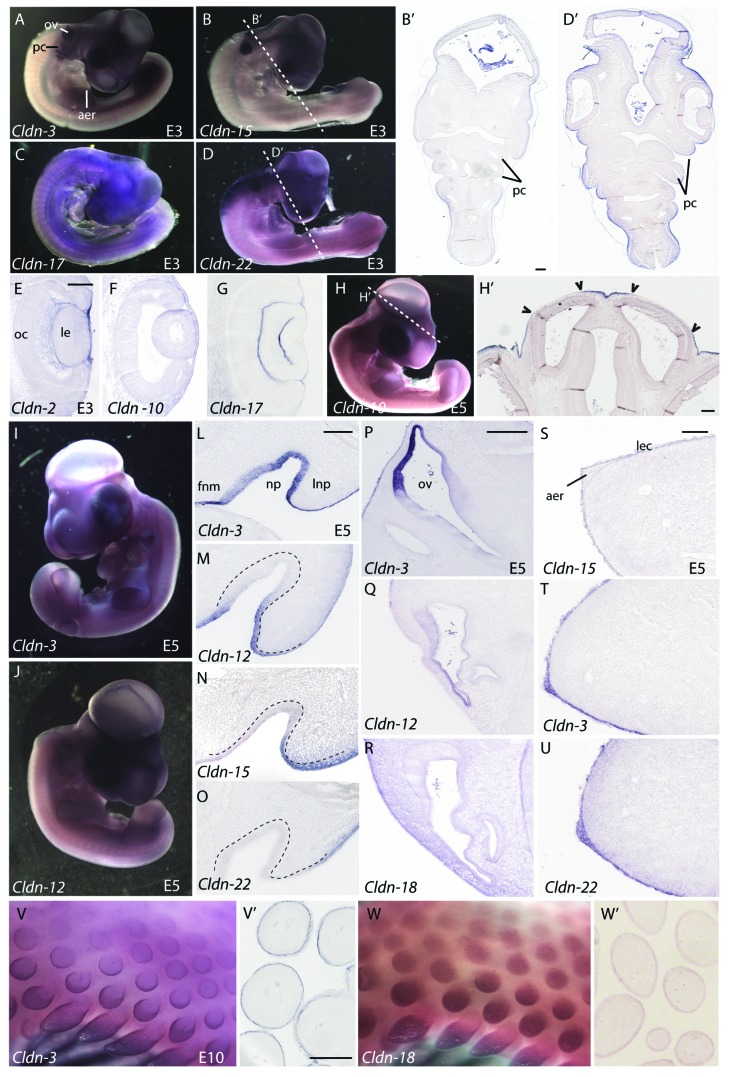
Figure 6. Expression of claudins in ectodermal derivatives. (A–D) Expression of claudins in E3 embryos. Whole mount views of E3 embryos showing expression of Claudin-3 (A), Claudin-15(B), Claudin-17(C) and Claudin-22(D). (B’, D’) Transverse sections taken at the level of the dashed lines indicated in B and D indicate boundaries of claudin expression observed in the surface ectoderm. (E–G) Claudin expression patterns in the eye. Sections through the head of Claudin-2 (E), Claudin-10(F) and Claudin-17(G) illustrate claudin boundaries in the surface ectoderm overlying the developing eye of E3 embryos. (H, H’) Expression of Claudin-10 in a whole-mount view and transverse section through the head at the level of the dashed line. Arrowheads indicate boundaries of expression in the surface ectoderm overlying brain ventricles. (I, J) Whole mount views of E5 embryos hybridized to a Claudin-3 or Claudin-12 riboprobe. (L–O) Claudin expression in the nasal pit of a E5 embryo. Representative examples of four expression patterns observed in the nasal pit. Dashed lines outline the position of the nasal epithelium. (P–R) Expression patterns of claudins the otic vesicle. (S–U) Claudin expression in the apical ectodermal ridge (AER). Claudin-15 is a representative example showing expression in the limb ectoderm, but no AER expression (S) as compared with Claudin-3 and -22, two examples of claudins highly expressed in the limb ectoderm and AER (T, U). (V, W) Expression of Claudin-3 and -18 in the feather buds of E10 embryos. Sections through the skin and feathers are shown in V’ and W’. All scale bars represent 0.1 mm. Abbreviations: aer, apical ectodermal ridge; fnm, frontonasal mass; le, lens; lec, limb ectoderm; lnp, lateral nasal process; np, nasal pit; oc, optic cup; ov, otic vesicle; pc, pharyngeal clefts.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.