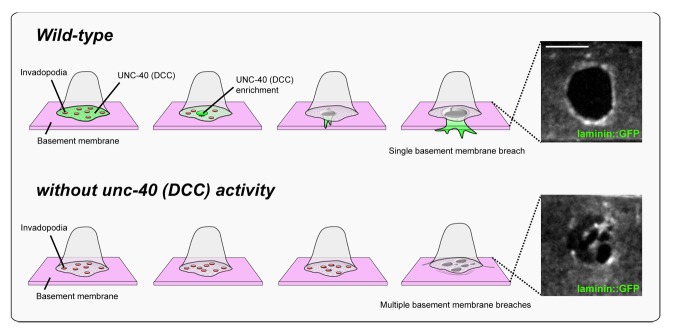
Figure 3. UNC-40 (DCC) focuses AC invasion through a single basement membrane breach. In wild-type animals, invadopodia (red circles) form and turn over until one breaches the basement membrane. UNC-40 (DCC, green) localizes to the breach site and directs the formation of a cellular protrusion, which guides invasion through a single large basement membrane breach into the vulval tissue (ventral view of laminin::GFP, right). As the protrusion grows, new invadopodia cease to form, thus inhibiting additional breaches. In the absence of the UNC-40 netrin receptor, the AC fails to build an invasive protrusion and invadopodia continue to form (bottom). Multiple breaching events occur resulting in numerous holes in the basement membrane (laminin::GFP, right).
