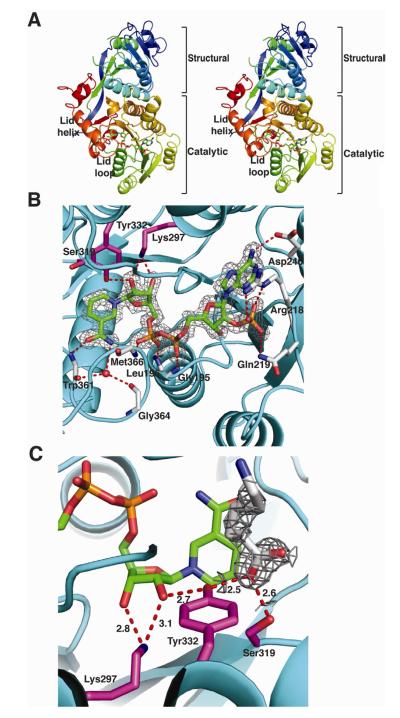
Figure 2. Structure of PlmKR1.
(A) Trace of the polypeptide chain from N- (blue) to C-terminus (red). The mobile lid helix and lid loop of the catalytic domain are labeled in the stereo image. The NADP+ cofactor is shown as sticks with atomic coloring (blue N, red O, yellow S and orange P) and green C.
(B) PlmKR1 active site and NADP+ density. Side chains of the catalytic residues (Tyr 332, Ser319, Lys297) are shown as sticks with magenta C. The NADP+ cofactor is shown as in A with the 2Fo-Fc electron density contoured at 1 σ. The residues that interact with NADP+ are shown as sticks with grey C. The conserved Trp332 of A-type KRs is shown with light red C. The ribbon diagram of the polypeptide has an orange structural domain and cyan catalytic domain.
(C) Density for 6-aminohexanoic acid. The 2Fo-Fc electron density for the 6-aminohexanoic acid is shown contoured at 1 σ. The 6-aminohexanoic acid is shown as sticks with grey C. Hydrogen bonds between active site residues, NADP+ nicotinamide ribose, and 6-aminohexanoic acid are shown in red. The catalytic residues are shown and colored as in B. The NADPH cofactor is shown as in A.